Why Greenland’s warming landscape is fueling geopolitical tensions
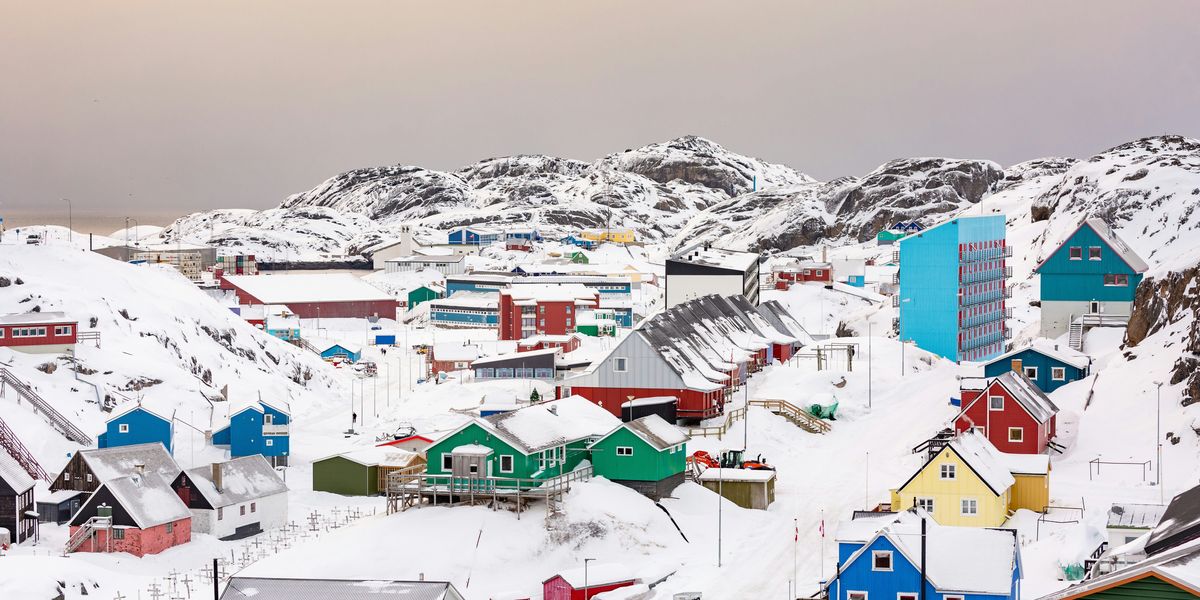
The warming climate has intensified global interest in Greenland, a resource-rich island whose melting ice sheet affects global sea levels and weather patterns.
Seth Borenstein reports for Associated Press
In short:
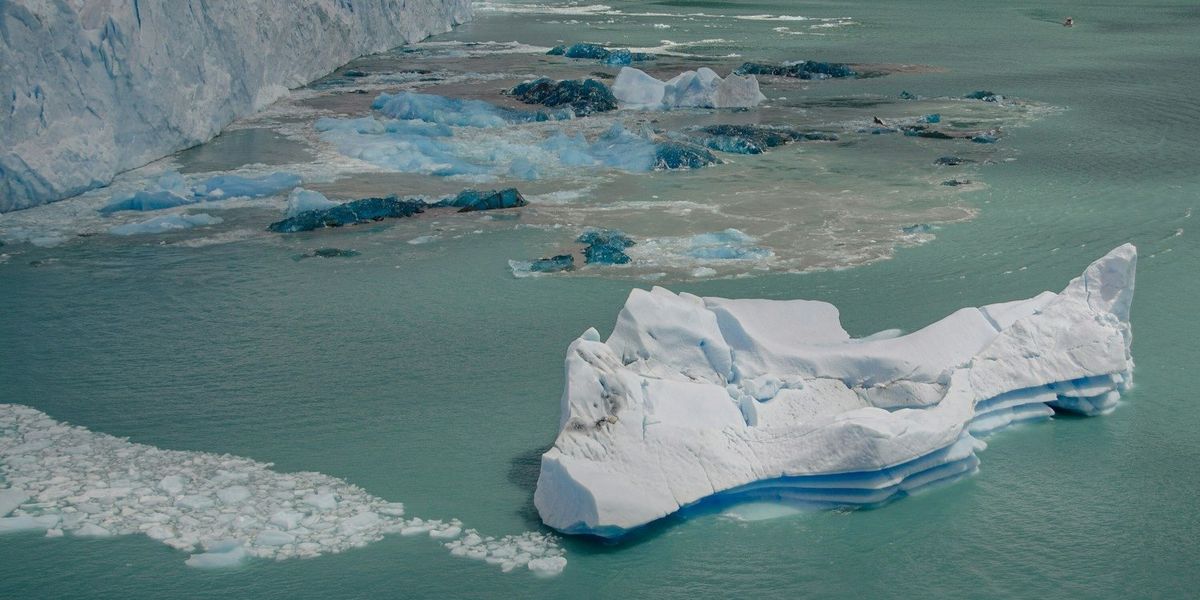
- Greenland’s ice sheet is melting at an accelerating rate, contributing to rising sea levels that could reshape coastlines globally.
- Donald Trump has repeatedly and aggressively stated interest in the U.S. acquiring Greenland, a longtime U.S. ally and semi-autonomous territory of Denmark.
- The island holds vast deposits of rare earth minerals, natural gas and oil, making it a geopolitical focus as nations compete for access to resources.
- Greenland’s melting ice impacts the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation, a crucial ocean current that regulates weather patterns across continents.
Key quote:
“If this global current system were to slow substantially or even collapse altogether — as we know it has done in the past — normal temperature and precipitation patterns around the globe would change drastically.”
— Jennifer Francis, climate scientist, Woodwell Climate Research Center
Why this matters:
The loss of Greenland’s ice could permanently alter coastlines and destabilize the climate, affecting ecosystems, agriculture and economies worldwide. As resource competition grows, Greenland is poised to play a central role in international relations.