US government toughens rules on chemicals used to break up oil slicks
In a nutshell:
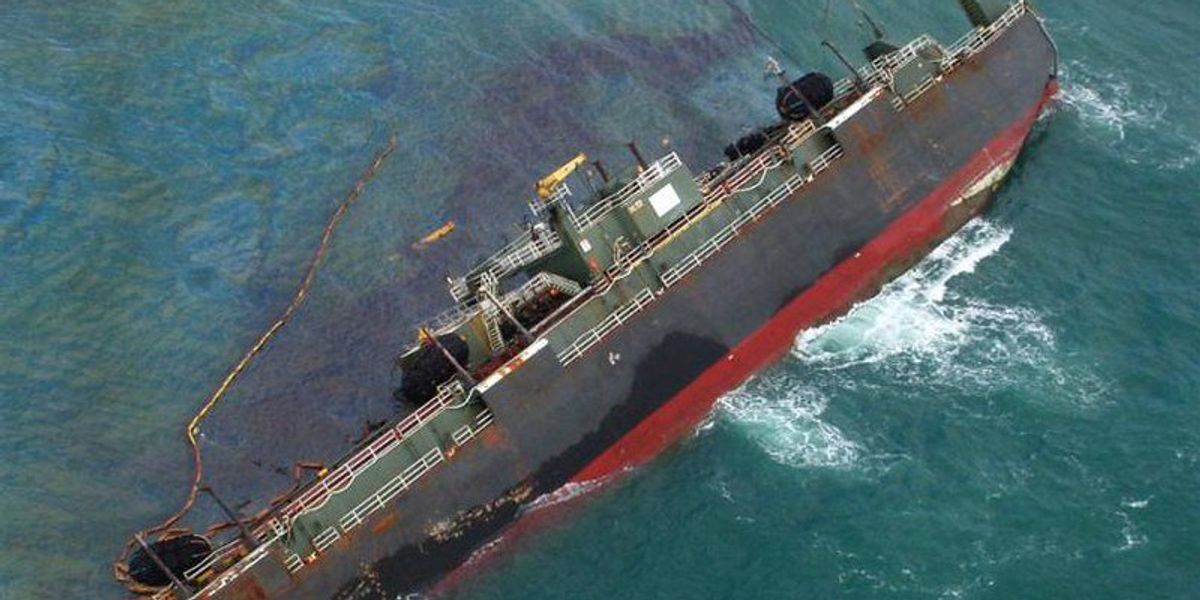
Chemicals used to break up oil slicks are getting a stringent makeover by the EPA as ongoing research continues to establish a link between exposure to chemical dispersants and myriad chronic illnesses suffered by Deepwater Horizon clean-up workers as well as those involved in the 1989 Exxon Valdez remediation. Exposure to dispersants has been linked to increased risk of cancer, cardiovascular damage and negative birth outcomes.
Key quote:
“What has happened to the BP workers and coastal residents with all these illnesses and lingering harm and sick and dying children. Nobody wants that to happen again,” said Riki Ott, an Alaska toxicologist.
Big picture:
A recent report by The Guardian disclosed that BP cleanup workers in the Gulf of Mexico were provided with training materials that alleged the dispersants being used contained no harmful ingredients — a blatant inaccuracy that the new regulations also seek to address. Furthermore the efficacy of dispersants decreases markedly in cold water which should give pause with more drilling planned for northern regions and a subsequent increase in cold-water oil transport. The EIS prepared for the Alaska oil lease by the Interior Department assumes a nearly 1 in 5 chance of a large spill in that region.
Read the full story in The Guardian.