elizabeth claire alberts
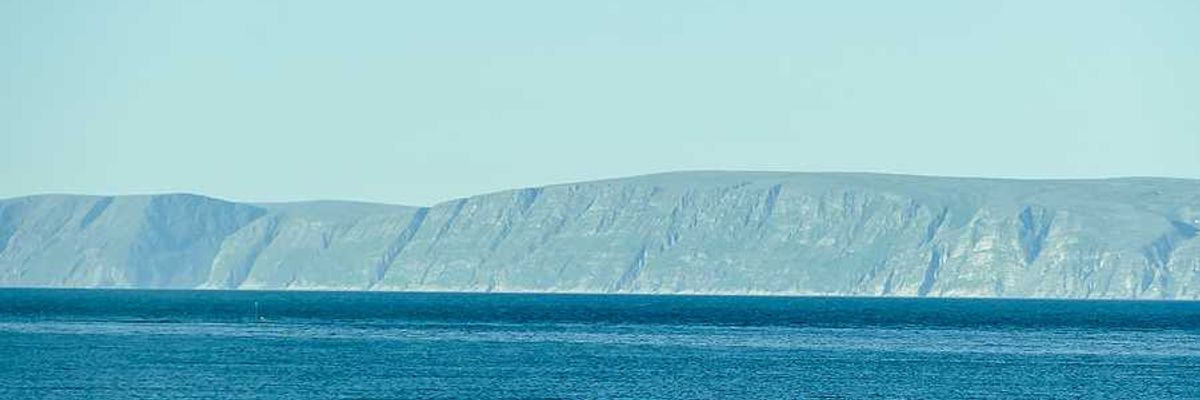
Acid test: Are the world’s oceans becoming too ‘acidic’ to support life?
The world’s oceans absorb about a quarter of humanity’s carbon dioxide emissions, buffering us against higher atmospheric CO2 levels and greater climate change. But that absorption has led to a lowering of seawater pH and the acidification of the oceans.
U.N. Ocean Conference ends with promises. Is a sea change coming?
Tropical trees’ growth and CO2 intake hit by more extreme dry seasons
A new study has found that dry seasons that are warmer and drier than usual can stunt the growth of tropical trees, causing them to take in less carbon dioxide.
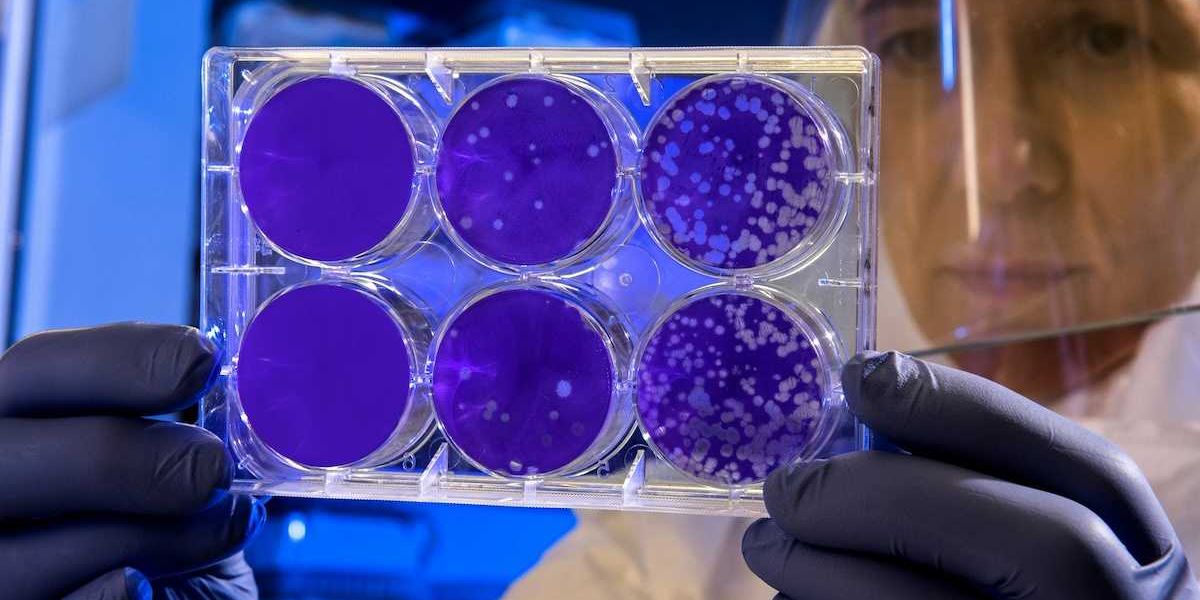
Seafloor microbes hoover up methane, keeping global warming in check
A new study found that carbonate rock mounds on the ocean floor host communities of microbes that actively consume methane, a greenhouse gas that is particularly potent if released into the atmosphere.
Climate change isn’t fueling algal blooms the way we think, study shows
A recent study found that there are no global trends that would suggest that climate change is having a uniform impact on harmful algal blooms throughout the world, although this is a commonly held belief.
Migratory freshwater fish in peril as report shows population plunge
Migratory freshwater fish are in big trouble. According to a new report, monitored populations of migratory freshwater fish have dropped on average by 76% since 1970, which is a higher rate of decline than among marine and terrestrial species.
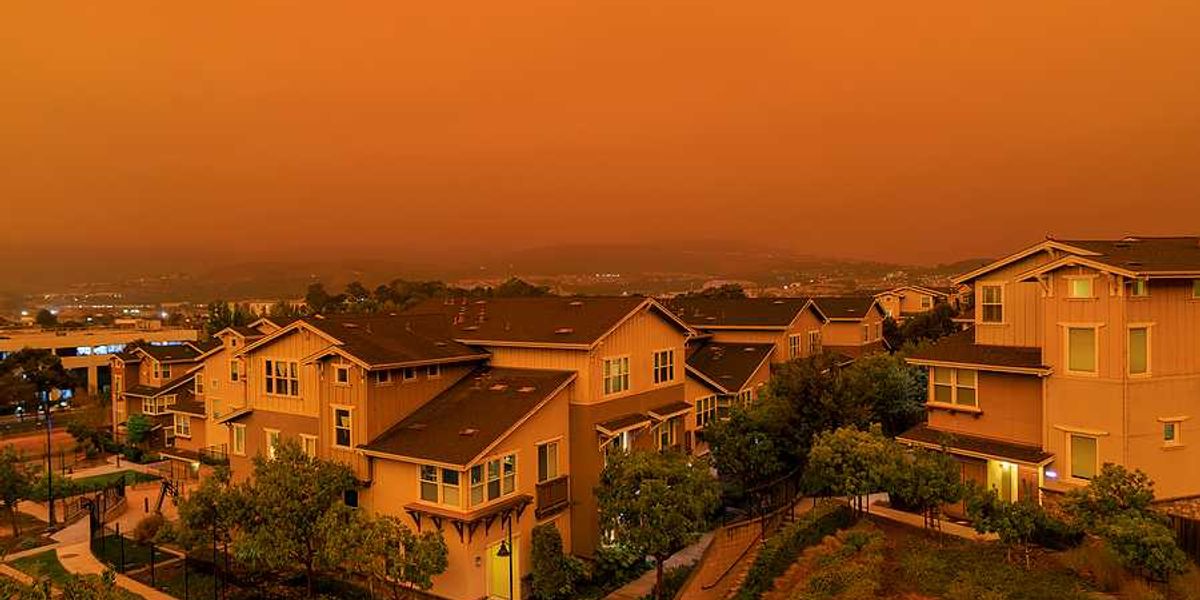
Siberia experiences hottest spring on record, fueling wildfires
In April, many parts of Asia, including Siberia, experienced record heat, which led to wildfires in Russia's northernmost region. The fires, which are likely fueled by climate change, could release more carbon dioxide into the air, which generates further warming, experts say.