Opinion: Supreme Court undoing 50 years’ worth of environmental progress
The Supreme Court has taken a brazen anti-regulatory turn. It’s our planet and health that will suffer.
For the past few months, Americans have faced multiple political distractions: Ukraine, inflation, AI, whether or not we intentionally nuke our own economy.
With all of these hyper-dramas, we quietly managed to harpoon some of the half-century-old cornerstones of environmental law.
How — and why — on Earth did we do that?
Supreme Court takes aim at wetlands
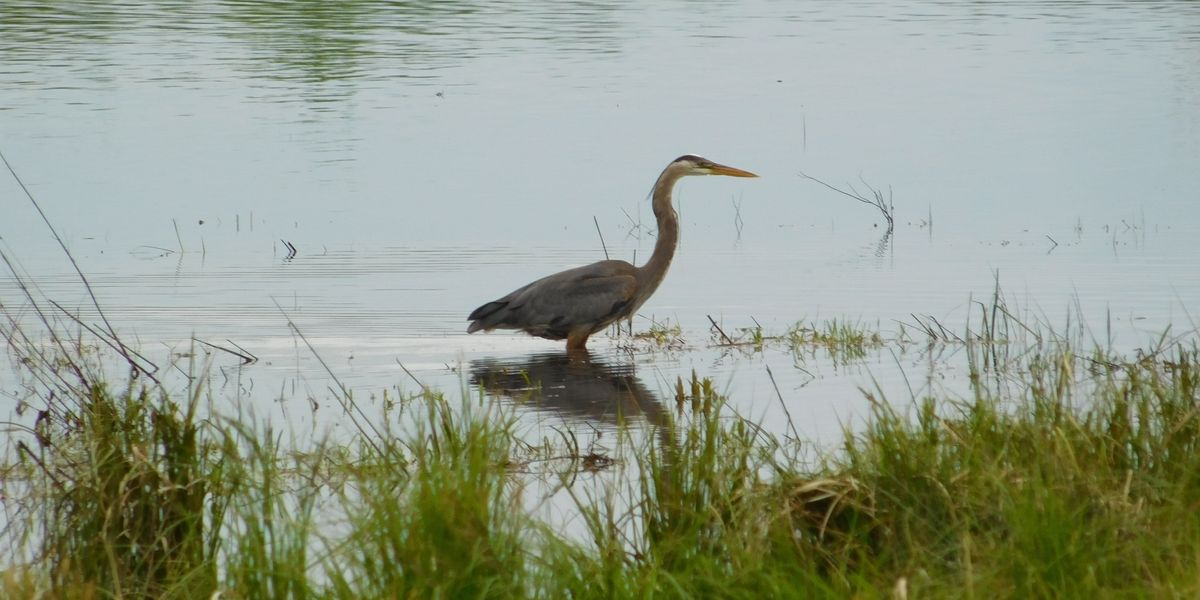
At the end of May, the Supreme Court took a major bite out of the Environmental Protection Agency's (EPA) ability to protect wetlands under the Clean Water Act. An Idaho couple initiated the case in 2007 when the Clean Water Act prevented them from building a home on a property that contained wetlands.
Over the next 16 years, Sackett v. EPA became the focal point for farmers, homebuilders, industrialists, anti-regulatory groups and many more who saw the EPA as an out-of-control federal agency.
Before a Supreme Court re-cast by three conservative Trump nominees, the 5-4 SCOTUS vote actually saw Trump nominee Brett Kavanaugh side with the court’s three remaining liberal justices. But the Sackett ruling played the same role for EPA politics that the 2022 Dobbs case did for neutralizing Roe v. Wade in abortion rights.
In June 2022, West Virginia v. EPA was another long-simmering case on the EPA’s ability to regulate power plants for greenhouse gas emissions. The court’s full 6-3 conservative majority ruled in favor of West Virginia Attorney General Patrick Morrisey and more than a dozen of his state colleagues. The decision monkey-wrenched the Biden administration’s ability to meet carbon reduction goals under the Paris climate accord.
But wait, there’s more! Also, in June 2022, a federal district court scored a win for environmental advocates by knocking down Trump administration rules limiting Endangered Species Act enforcement. That one, or other Endangered Species Act cases, will fall into the lap of SCOTUS sooner rather than later.
SCOTUS anti-regulatory turn
Justice Elena Kagan has been a consistent voice of futile outrage over the Court’s anti-regulatory turn. In a dissent to the Sackett decision last week, she wrote that the Court’s majority had its “thumb on the scale” of justice.
With Trump’s three relatively young lifetime appointees, SCOTUS seems locked into a generation of anti-regulatory, pro-business judgment. And the judicial undercard? In his single term, Trump made 54 appeals court and 174 federal court picks, effectively tying up much of the federal courts system before reaching the Supreme Court.
By now, surely you must be thinking it’s a good thing that there are two other branches of government. But no. Not this week.
Debt limit giveaway to oil and gas
As a major giveaway in the compromise to raise the debt limit, President Biden and the congressional Democrats agreed to “streamline” the permitting process for energy projects. That meant weakening the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA), another key law from 1970. NEPA required an environmental impact statement for any consequential development using federal land or funds.
Oil and gas pipeline projects would benefit deeply and quickly, as would methane export projects and new plastics factories stateside, with appeals and public comment periods shortened.
It was progressive Rep. Jared Huffman who told the Washington Post, “They must think we’re really, really stupid,” (if Republican leaders thought the Dems’ leaders would agree to this).
Then, the Democrats did agree to it.
The environment as a political pawn
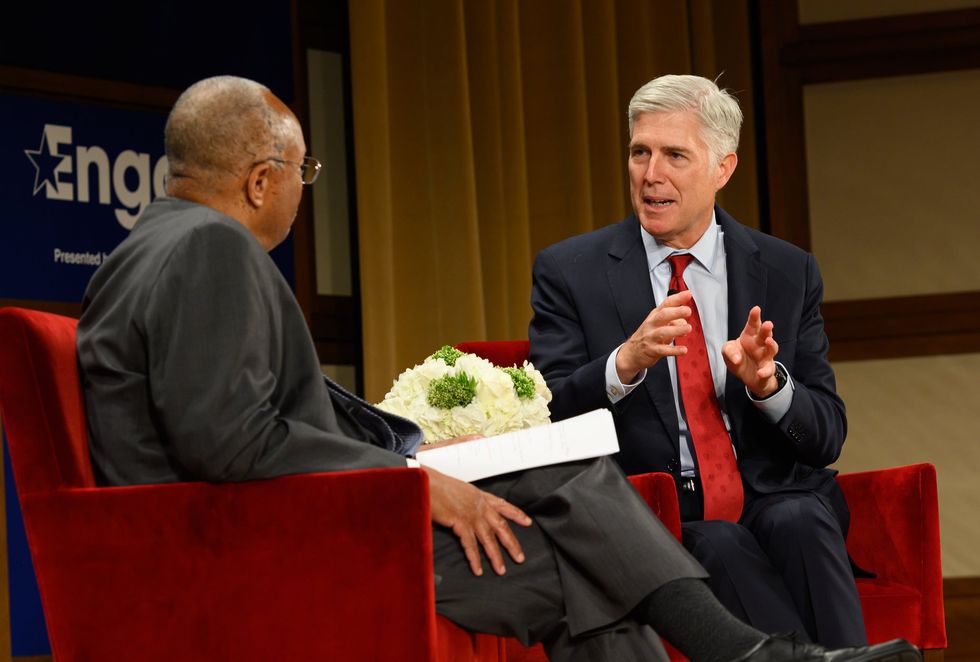

US Supreme Court Justice Neil Gorsuch in 2019. Gorsuch's mom, Anne Gorsuch Burford, was Ronald Reagan’s first EPA administrator and was openly hostile to the agency she ran.
Credit: George W. Bush Presidential Center/flickr
I’m afraid that this illustrates just how little clout environmental issues still have. Even as we proclaim climate change an “existential” threat, it’s one of the first items tossed under the bus.
It’s a far cry from the time when the high court had its own treehugger. Justice William O. Douglas served 36 years on the court. He once asked during a case involving a ski resort if trees should have the same rights as humans.
Today’s court has a bizarre, mirror-image environmental twist of its own. Justice Neil Gorsuch was the first of Trump’s appointees. His mom, Anne Gorsuch Burford, was Ronald Reagan’s first EPA administrator. She openly expressed contempt for the agency’s mission and was forced out by scandal after two years.
Now her son and other Trump appointees are taking up her cause — and it’s our planet that will suffer.