Global renewable energy has quadrupled over past decade
With solar leading the way, clean energy capacity growth is helping the planet avoid billions of tons of carbon dioxide emissions each year.
Renewable energy capacity quadrupled across the planet over the past decade and energy from solar power increased 26 times from what it was in 2009, according to an international report released today.
The Global Trends in Renewable Energy Investment 2019 report finds renewables accounted for 12.9 percent of global electricity in 2018—up from 11.6 percent in 2018. (The report excluded hydroelectric power, which, if included, bumps the current renewable share to 26.3 percent of total electricity produced.)
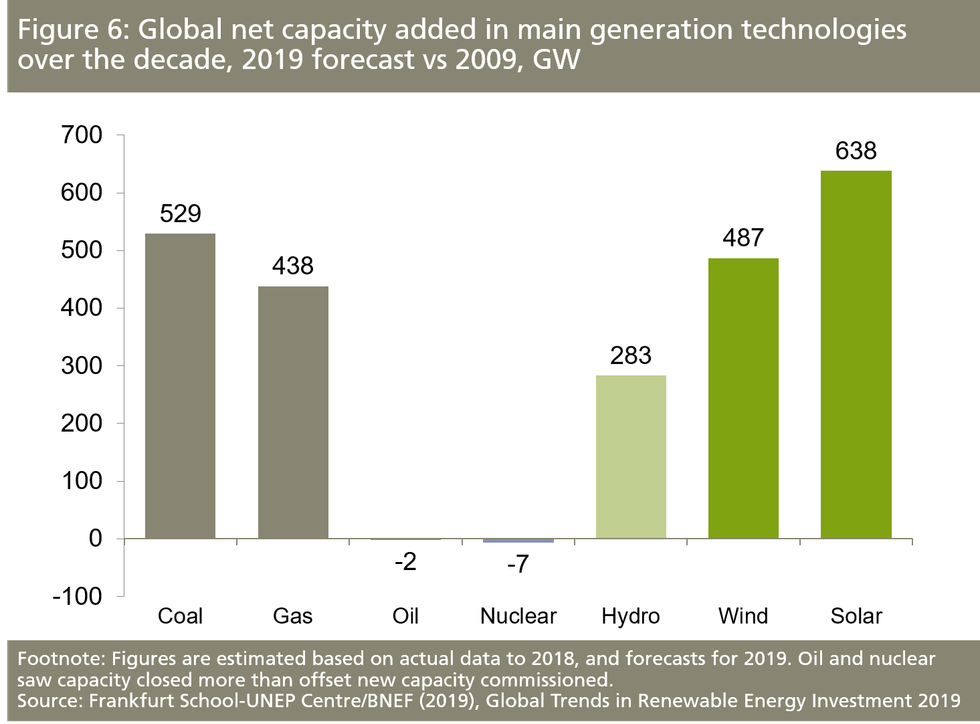
The 1.2 terawatts of new renewable energy capacity added over the past decade is "more than the entire electricity generating fleet of the U.S. today," the authors wrote.
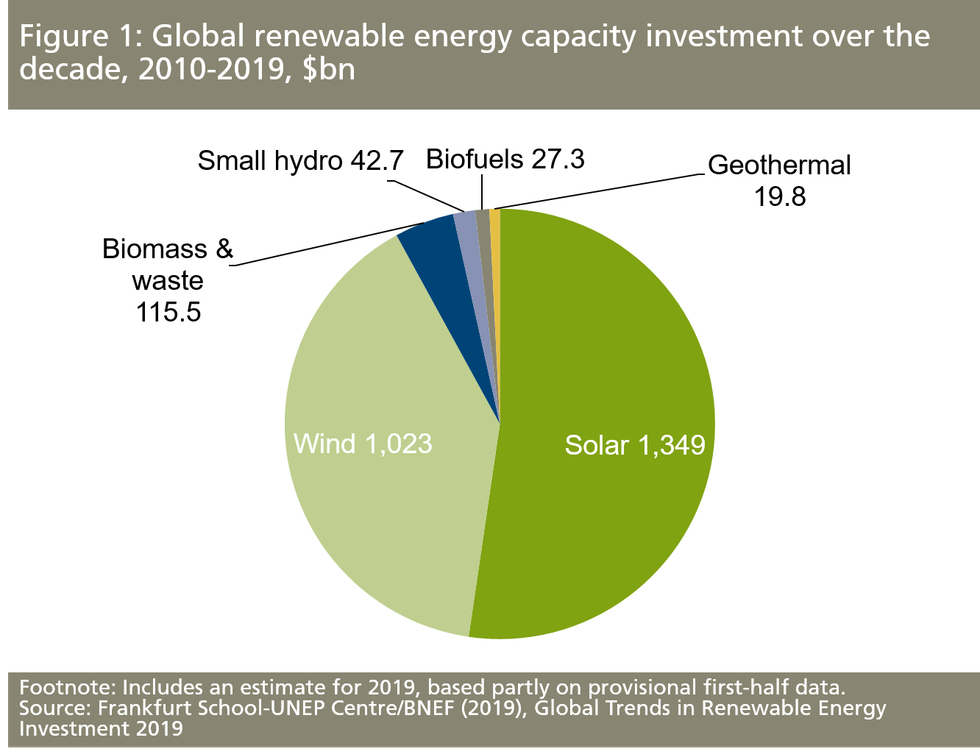
This continued growth—led by solar, which accounts for about a quarter of all renewable energy and was the most added energy source of any kind during the period studied—gave the planet a reprieve from an estimated 2 billion tons of carbon dioxide emissions last year. With capacity growing and global investments at more than $2.6 trillion, the report shows momentum for clean energy continues in most countries.
"Investing in renewable energy is investing in a sustainable and profitable future, as the last decade of incredible growth in renewables has shown," said Inger Andersen, Executive Director of the UN Environment Programme, in a statement. The UN Environment Programme produced the report along with the Frankfurt School-UNEP Collaborating Centre for Climate & Sustainable Energy Finance and BloombergNEF.
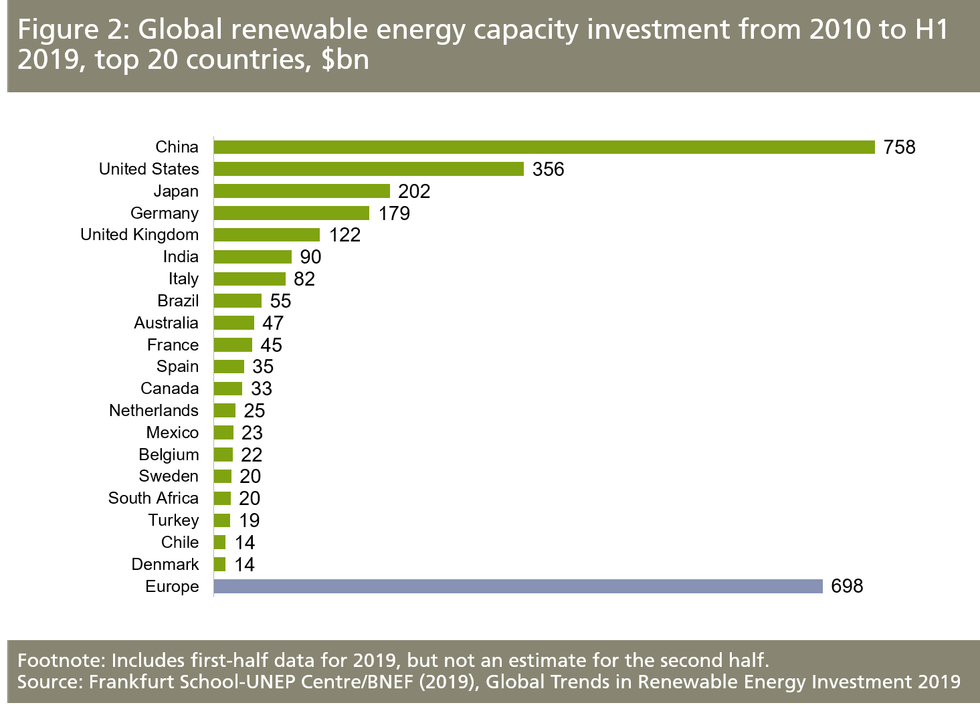
Total investment over the past decade was roughly $2.6 trillion, with half of that dedicated to solar. China led the way in renewable investment, committing about $758 billion between 2010 and early 2019. The U.S. was second to China, committing less than half that amount over the same time—$356 billion.
Japan was third, investing $202 billion, and Europe, as a whole, invested about $698 billion.
Developing countries, excluding China and India, invested about $47.5 billion in added capacity in 2018—a 22 percent increase over the previous year and the highest total for a single year ever.
Vietnam's renewable energy capacity investment, for example, increased ninefold from 2017 to 2018, reaching $5.2 billion.
Report authors pointed to the increasing affordability for wind and solar.
"Sharp falls in the cost of electricity from wind and solar over recent years have transformed the choice facing policy-makers," said Jon Moore, Chief Executive of BloombergNEF, in a statement. "These technologies were always low-carbon and relatively quick to build. Now, in many countries around the world, either wind or solar is the cheapest option for electricity generation."
The report, released ahead of the UN Global Climate Action Summit later this month in New York City, wasn't all good news, it found: global investments in renewable energy decreased 12 percent from 2017 to 2018, fossil fuel subsidies continue to "run into the hundreds of billions of dollars each year," and that 1.1 billion people are still without electricity.
The dip in investments was specific to added energy capacity and largely linked to lower equipment costs and China tariffs for solar projects. Corporate and government investment into research and development, for example, both rose in 2018 over the previous year.
The authors, while optimistic, said sustained renewable energy progression needs to continue if the planet is to avoid the worst potential impact from climate change.
"We cannot afford to be complacent," said Inger Andersen, Executive Director of the UN Environment Programme, in a statement. "Global power sector emissions have risen about 10 percent over this period. It is clear that we need to rapidly step up the pace of the global switch to renewables if we are to meet international climate and development goals."