Climate pollution from plastics to outpace coal emissions in US by 2030, report finds
The petrochemical industry has found a new market for fossil fuels: plastics."
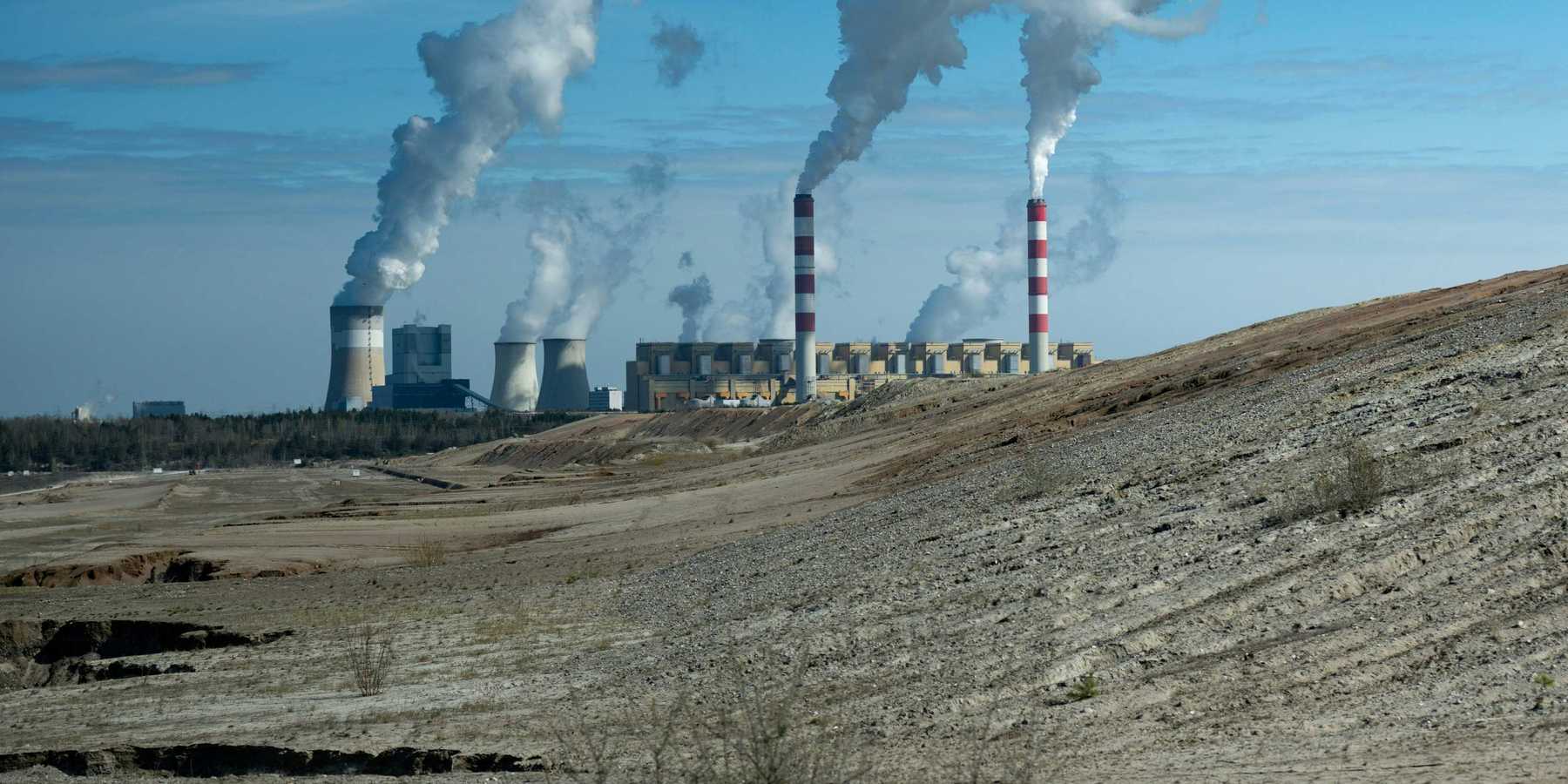
With dozens of new plastics manufacturing and recycling facilities in the works, the U.S. plastics industry will release more greenhouse gas emissions than coal-fired power plants by 2030, say the authors of a new report.
Emissions from the plastics sector equaled that of 116 coal-fired power plants last year, according to the report out Thursday from Bennington College's Beyond Plastics project. Meanwhile, 42 plastics manufacturing and recycling facilities have opened, or are in the process of being built or permitted, since 2019.
“As the world transitions away from fossil fuels for electricity generation and for transportation, the petrochemical industry has found a new market for fossil fuels: plastics," Judith Enck, president of Beyond Plastics, told reporters on Thursday.
With the U.S. coal industry in decline, the report authors say policymakers at home and at the upcoming COP26 climate summit, a conference happening at the end of month where world leaders will hash out the details of climate pledges, need to factor the climate toll of plastics into emissions reductions efforts.
“Leaving out plastics is leaving out a giant piece of the problem," Enck said. “We would like the national leaders that are gathering in Glasgow, Scotland, to take the plastics issue just as seriously as they are taking transportation and electricity generation."
Climate costs of U.S. plastics
The report authors calculated emissions from 10 stages of plastics production, from hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, for the raw material—ethane in natural gas—all the way up to burning waste in incinerators.
Cracker plants, where natural gas is heated at such high temperatures that it fractures into plastic building blocks like ethylene, have the heaviest emissions toll, producing around 70 million tons of carbon dioxide-equivalent pollutants, which is equal to the emissions of 35 coal-fired power plants. Because the report looks at emissions from a range of greenhouse gases, the authors converted the warming potential of all the pollutants into an equivalent amount of carbon dioxide, the most common greenhouse gas.
The authors say that emissions reports from the plastics industry are incomplete as they don't adequately account for leaks of methane—a greenhouse gas that's 84 times more climate-warming than carbon dioxide in the short-term—and other gases from the transport and production of plastics feedstocks.
Related: The US falls behind most of the world in plastic pollution legislation
They note that while so-called "chemical recycling," which uses large amounts of energy to melt used plastics into building blocks for fuel and other products, is uncommon now, new plants could add up to 18 million tons of carbon dioxide-equivalent pollutants by 2025. Enck referred to chemical recycling as plastics' "new deception" now that Americans are aware that less than 9% of plastics are recycled.
Shipping resins and other plastics building blocks overseas accounts for a significant amount of emissions as well, said Jim Vallette, president of Material Research, the firm that Beyond Plastics hired to do the report analysis. "Plastic is very much like the new coal because the coal industry also is counting on exports to stay alive," he added.
Harmful plastics pollution
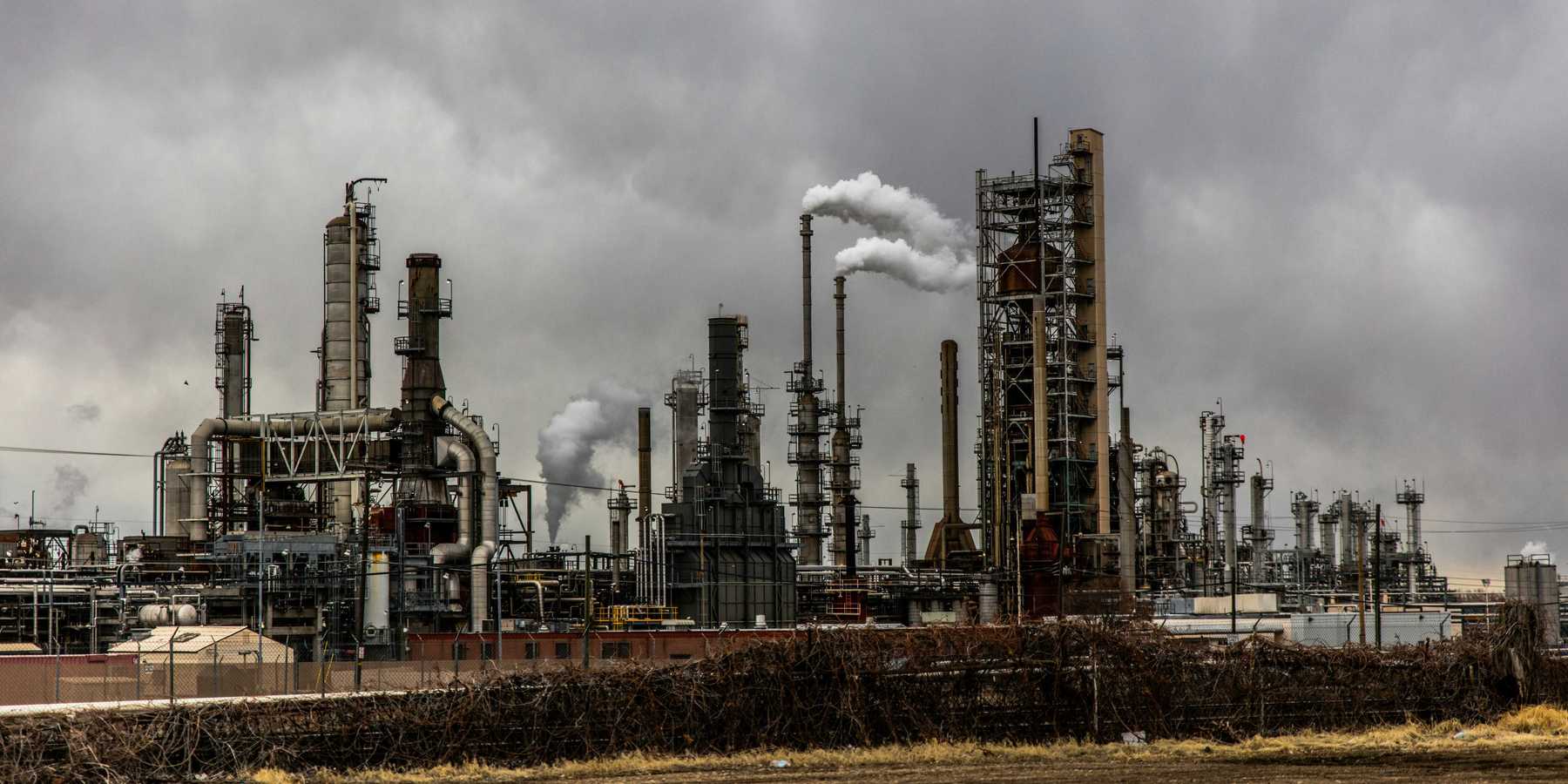
Plastics facilities don't just create planet-warming greenhouse gas emissions. They also release benzene, formaldehyde, and the carcinogen ethylene oxide, among other harmful pollutants. The plastics industry has come under fire in recent years for building its polluting plants in poorer parts of the country: 90% of the climate pollution from U.S. plastics plants occurs in just 18 communities that are mostly in Texas and Louisiana, according to the report.
"The health impacts of the emissions are disproportionately borne by low-income communities and communities of color, making this a major environmental justice issue," Enck said.
Banner photo credit: Bob Doran/flickr