This diet will likely keep you alive longer — and help the planet
New research finds the Planetary Health Diet lowers our risk to most major causes of death.
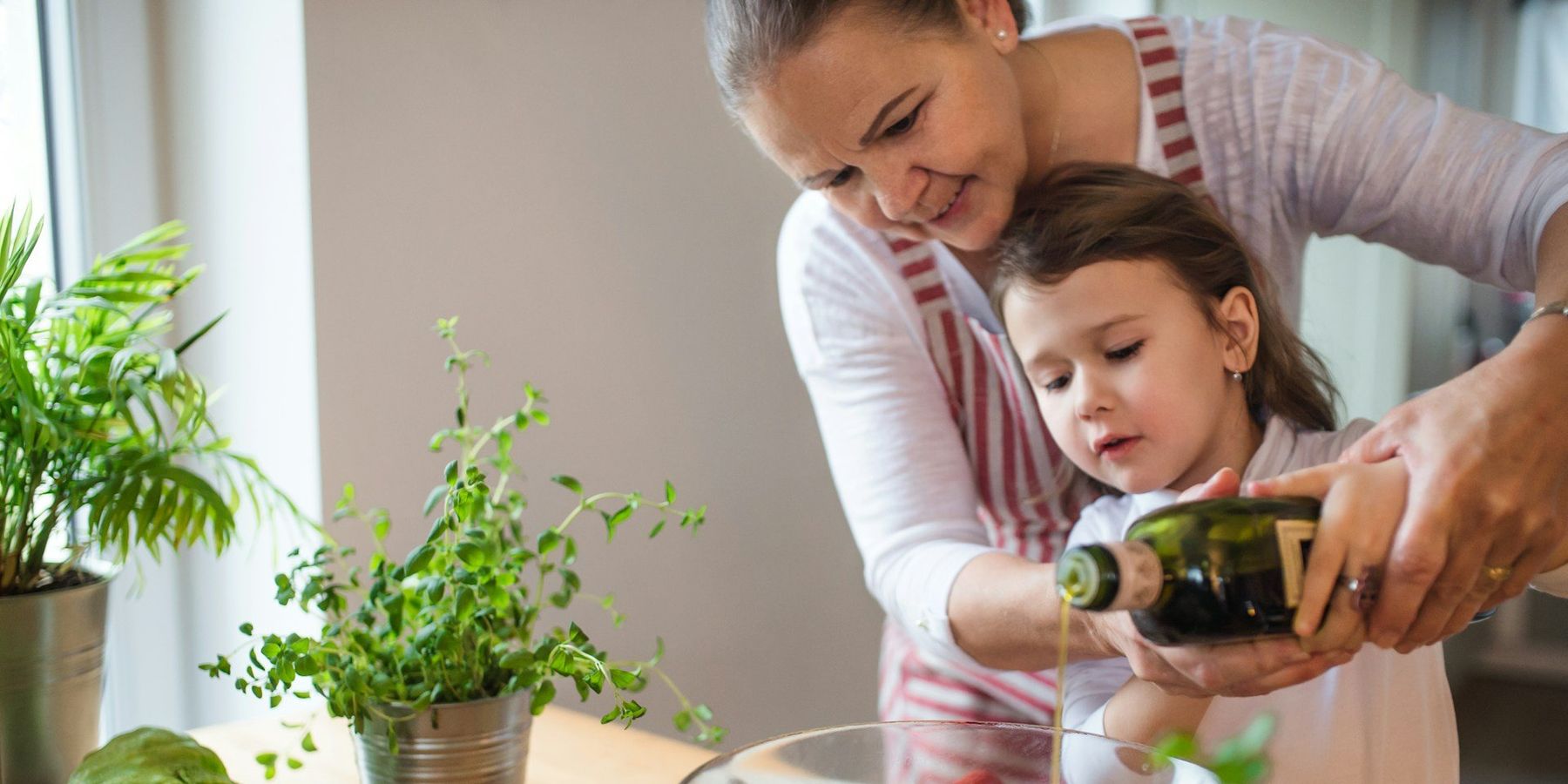
People who closely follow an environmentally conscious plant-heavy diet that also includes modest portions of meat and dairy, dubbed the Planetary Health Diet, have a 30% lower risk of premature death from common causes such as cancer and heart disease, according to new research.
The study, led by the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health and published today in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, suggests that our diets can play dual roles of saving us and the planet.
“Climate change has our planet on track for ecological disaster, and our food system plays a major role,” said corresponding author Walter Willett, professor of epidemiology and nutrition at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, in a statement. “Shifting how we eat can help slow the process of climate change. And what’s healthiest for the planet is also healthiest for humans.”
The EAT-Lancet Commission created the diet as part of a 2019 report that outlined how to feed a growing planet in a healthy way and avoid exacerbating climate change and environmental impacts from food production. It is “a plant-forward diet where whole grains, fruits, vegetables, nuts and legumes comprise a greater proportion of foods consumed.” It avoids most processed and ultra-processed foods, but still allows for meat and dairy consumption.
"What’s healthiest for the planet is also healthiest for humans.” - Walter Willett, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health
The diet suggests that roughly half of your plate should be fruits and vegetables, and the other half should be nearly all whole grains or plant protein. Dairy, animal proteins, starchy vegetables (like potatoes) and sugars are allowed in smaller portions.
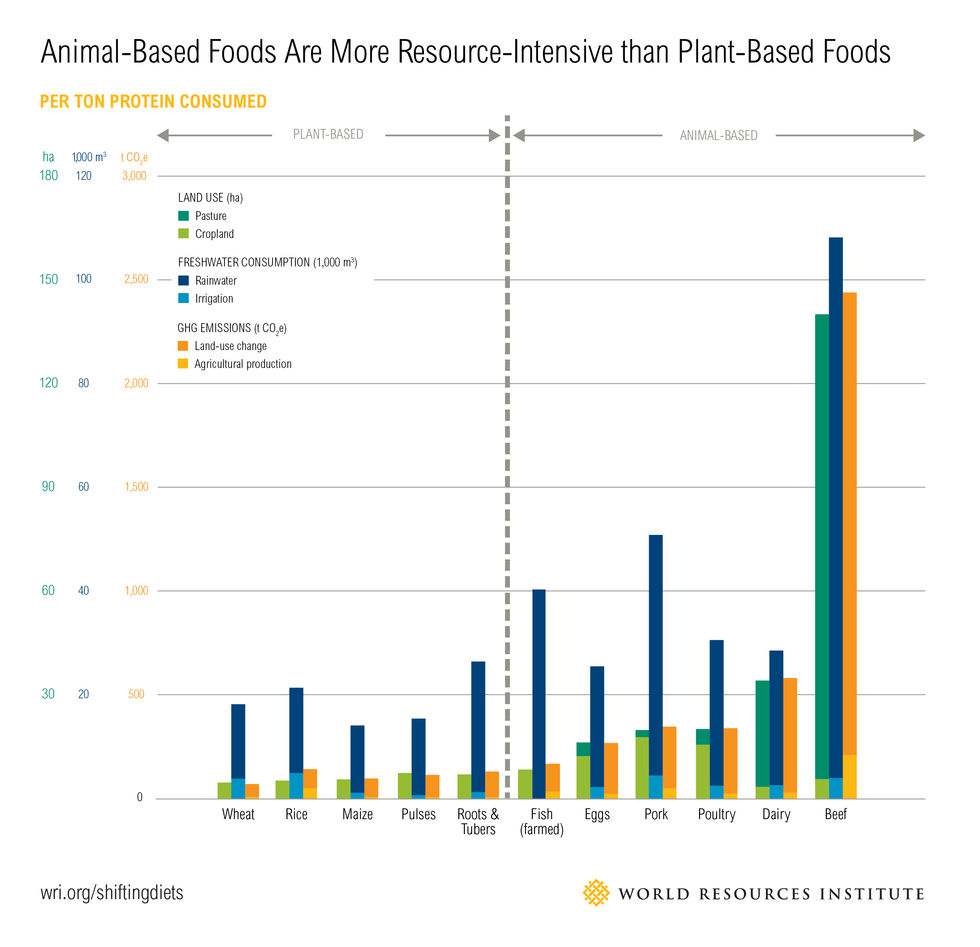
The plan goes beyond diet and encourages regenerative farming and cooking at home rather than eating out. Its focus on plant-based foods is aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions from livestock. Research shows transitioning to plant-based diets could reduce diet related land-use by 76% and greenhouse gas emissions by 49%.
Willett and colleagues examined data from more than 200,000 people who were disease-free at the start of the study. Each participant completed questionnaires about their diets and health every four years for up to 34 years.
The 10% of people that most closely followed the Planetary Health Diet had a 30% lower risk of premature death compared to the 10% of people in the group that least followed the diet. The researchers also estimated that those most closely following the diet had contributed 29% fewer greenhouse gas emissions, 21% lower fertilizer needs and 51% lower cropland use compared to those who followed the diet the least.
“Our study is noteworthy given that the U.S. Department of Agriculture has refused to consider the environmental impacts of dietary choices and any reference to the environmental effects of diet will not be allowed in the upcoming revision of the U.S. Dietary Guidelines,” said Willett. “The findings show just how linked human and planetary health are.”
See the full study here, and learn more about the Planetary Health Diet.













