Global electricity access grows—but we're not on track for 2030 sustainable energy goals
International report points to progress on electricity access, but finds clean cooking solutions and renewable energy in transportation and heating need to be bolstered.
More people on the planet have access to electricity than ever before, however, the world is on pace to fall short on the goal of affordable and sustainable energy for all by 2030, according to an international report on the state of international energy.
Meeting that goal, which was set as part of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, will require innovative solutions— such as solar lighting and full-home systems, as well as mini-grids—to serve the poorest and hardest to reach people, the authors wrote.
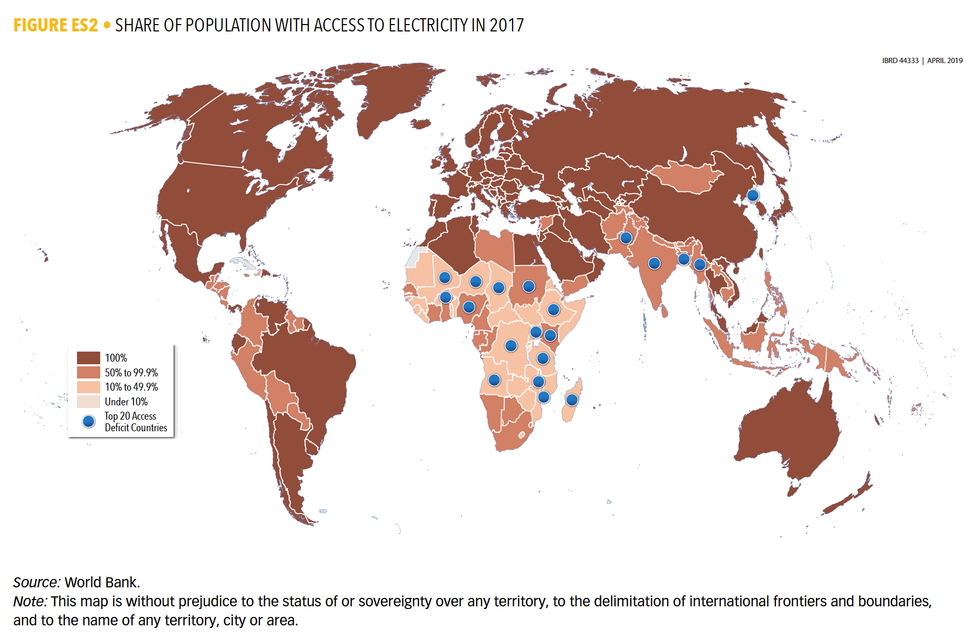
The Energy Progress Report released today found about 840 million people (about 11 percent of the people on the planet) now live without electricity, which is down from 1 billion in 2016, and 1.2 billion in 2010. Most of the progress over the past few years in connecting people was made in India, Bangladesh and Kenya.
Despite this progress, there is still a rural-urban divide: with the rural access rate at 79 percent, compared to 97 percent in urban areas.
A bulk of those without electricity—573 million—are in Sub-Saharan Africa, which is home to the 20 countries with the lowest rates of electricity.
"I am particularly concerned by the dramatic lack of access to reliable, modern and sustainable energy in certain parts of the world, especially in sub-Saharan Africa, a region where we need to really concentrate our efforts," Fatih Birol, the Executive Director of the International Energy Agency, said in a statement. The report is authored by the International Energy Agency, International Renewable Energy Agency, United Nations, World Bank and World Health Organization.
Each year between 2015 and 2017 about 153 million people gained access to electricity. If this rate continued, the 2030 UN goal of universal electricity would be reached, according to the report, however, "connecting the last of the unserved populations may be more challenging than past electrification efforts," the authors wrote.
They added: "Given the many challenges facing access-deficit countries, the latest projection places the access rate in 2030 at 92 percent, leaving 650 million people around the world without access to electricity."
About 90 percent of those projected to be without electricity in 2030 would be in Sub-Saharan Africa.
Renewable growth, room for improvement
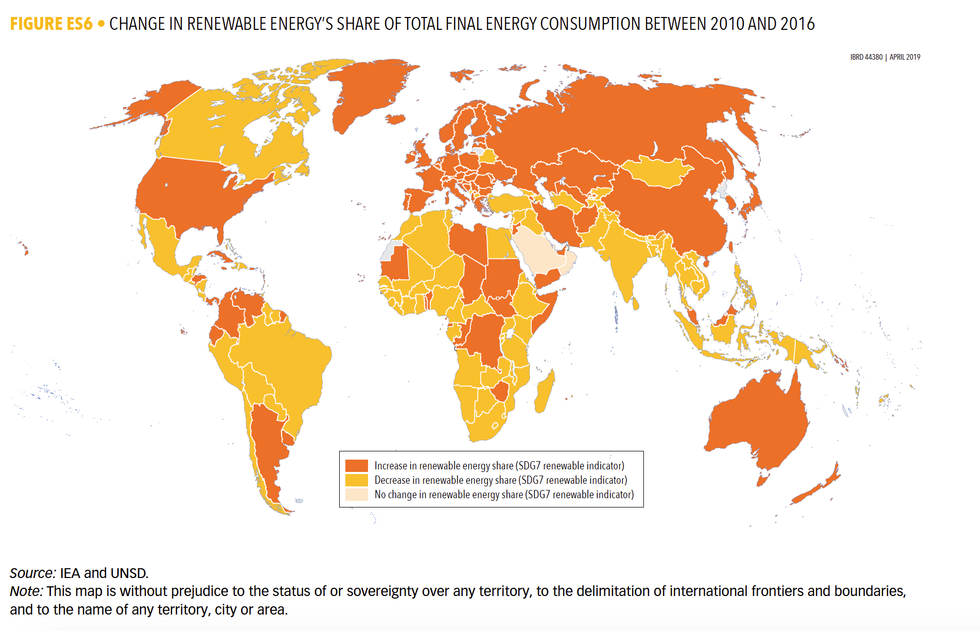
The report found about 17.5 percent of global energy consumed in 2016 was from renewable sources, which was up from 16.6 percent in 2010. The number of renewables used in electricity grew at its fastest rate in nearly 30 years—largely driven by Latin America hydropower, China's "record-level" wind capacity added in 2015; and solar growth in China and the U.S.
Hydropower is by far the largest source of renewable electricity, accounting for 68 percent.
While renewable gains continue in electricity, increases are slower in the transportation and heating sectors.
Renewables accounted for about 24 percent of heat generated, however, most of that comes from biomass, not "modern renewables" (such as wind, solar and geothermal, which only accounted for about 9 percent of heat generated). In transportation, renewable energy accounted for just 3.3 percent.
While, on the whole, there are increasingly renewable-friendly policies across the world and solar and wind technology costs are coming down, the authors say investment and political backing need to further expand.
"A substantial further increase of renewable energy is needed for energy systems to become affordable, reliable, sustainable, focusing on modern uses," the authors wrote.
Dirty cooking fuels
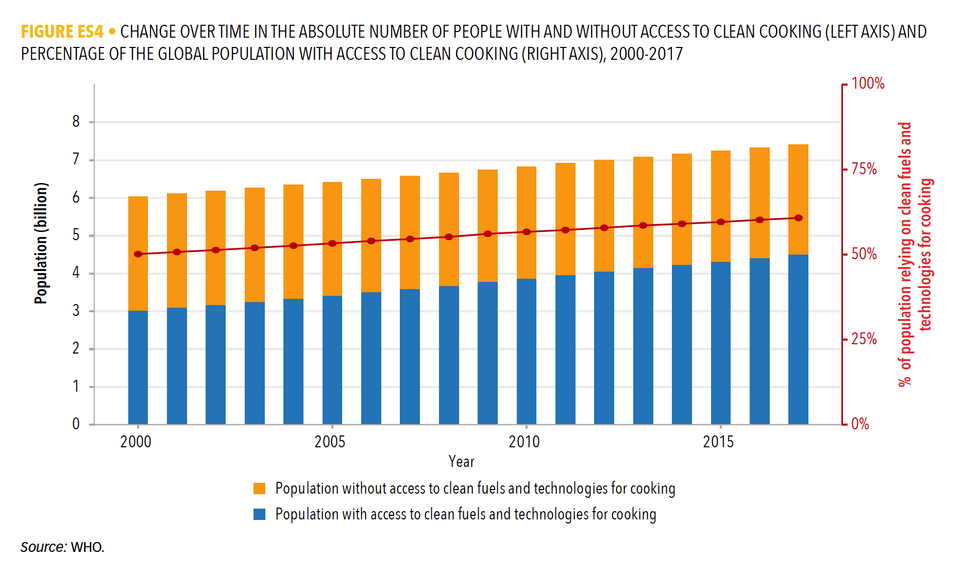
The report also found about three billion people, mostly in Asia and Africa, lack access to clean cooking solutions, and rely on heavy polluting fuels.
The percentage of the population with access to clean cooking fuels actually increased from 57 percent in 2010 to 61 percent in 2017, but the gains were offset by population growth.
"This poses a big threat to health and exacerbates inequality, especially towards women and children," Dr. Maria Neira, Director of Department of Public Health, Environmental and Social Determinants of Health for the World Health Organization, said in a statement.
A bulk of those lacking access to clean fuels are in Central and South Asia, and Sub-Saharan Africa.
The report estimates dirty cooking fuels, and the resulting indoor air pollution, will remain the cause of "millions of deaths" from diseases such as heart disease, stroke, and cancer.
See the full report here.