A global I-told-you-so
Forty years ago, Jimmy Carter's Global 2000 report sounded dire warnings about our environment.
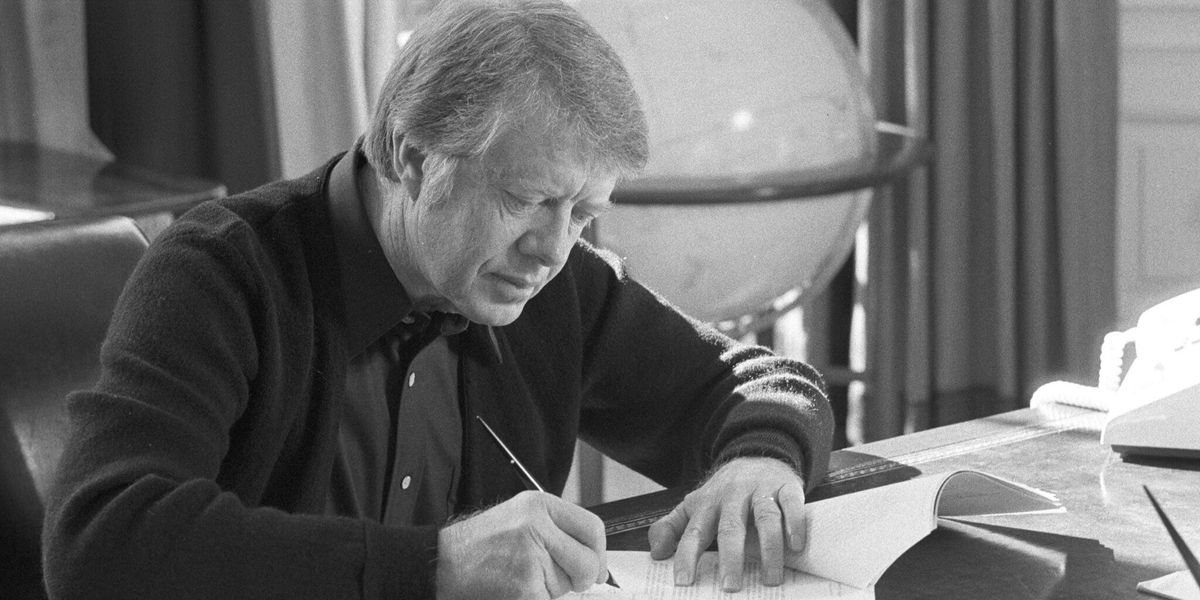
In 1977, the new president, Jimmy Carter, thought it might be nice to look ahead at what the global environment might look like at the dawn of the coming millennium.
The result was a report that was both exhaustive and alarming. Global 2000 was released to the public on July 24, 1980.
Twenty years into the 21st Century, the dire assessments of Global 2000 look startlingly accurate, and our failures at acting on them look every bit as startlingly bad. The report nailed it on predicting increases in air and water pollution in developing nations.
By 2000, India and China were already smoky poster children for the world. Both are still shamefully coal-reliant today. Greatly increased standards of living have drifted in with the smoke. Higher consumption levels came along as a result. The establishment of a middle class, particularly in China, has enabled hundreds of millions to pursue status symbols, like patent medicines made from endangered rhinos and tigers; and the inexplicably bland shark fin soup.
Fisheries in general are as bad or worse than laid out in the three-volume 1980 report. So are forests. Arable lands will soon be hard-pressed to feed booming populations.
Global 2000 understandably whiffed by a few crises that few saw coming: acidifying, plastic-choked oceans most prominent among them. If the report were written today, nuclear power would not receive as much attention as it did in 1980.
Perhaps that shouldn't be a surprise, since it came out a mere 16 months after the near-calamity at the Three Mile Island nuclear power plant in Pennsylvania.
"The projected production of increasing amounts of nuclear power" was thwarted by a quadruple threat—massive public protests, cold feet on Wall Street, two true calamities at Chernobyl (1986) and Fukushima (2011), and the availability of cheaper electricity largely from natural gas.
Fossil fuels in general are presumed to have a permanent birthright, with hints at the coming birth of clean energy. There are no hints that clean energy has a 40 year gestation period.
Climate lite
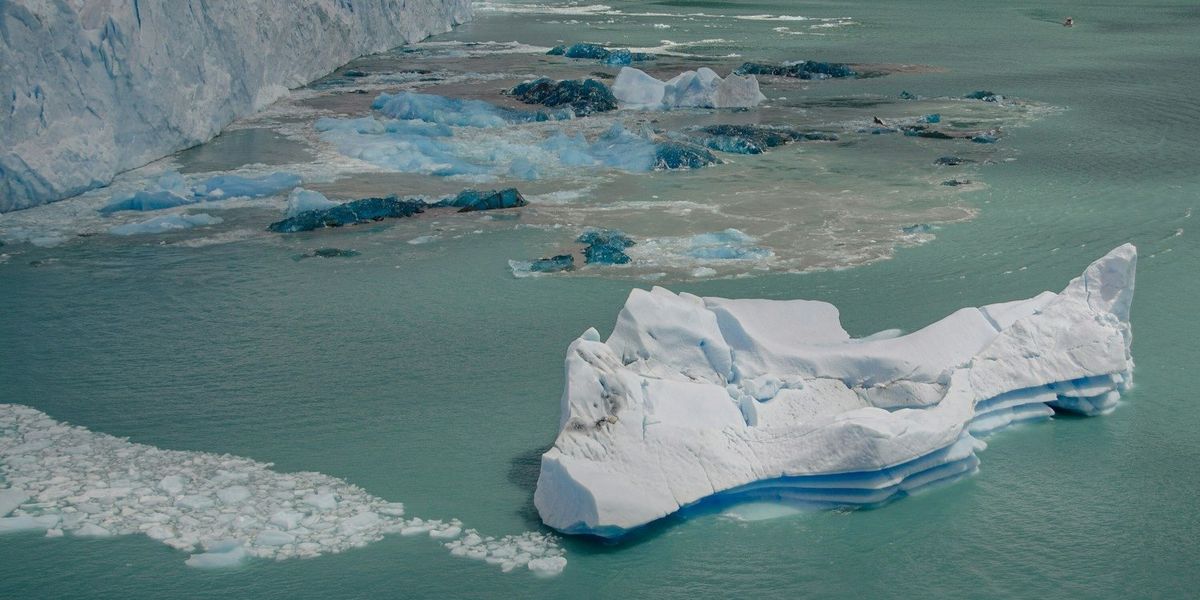
One area where Global 2000 treads lightly is in climate change. Bear in mind that the report preceded the first major focus on climate by eight years—NASA scientist James Hansen's riveting 1988 testimony before Congress. Nevertheless, our Carter-era climate science foresaw the possibility of melting polar ice caps "forcing the (eventual) abandonment of coastal cities."
Of course, once Miami Beach bids farewell to the existential threat of coronavirus, it can resume worrying about South Beach turning into the world's trendiest tidal flat.
The one that didn't get away
Global 2000 was an early alarm bell for the ozone layer, citing the ozone-depleting qualities of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) in destroying the Earth's stratospheric ozone layer. Within a decade of the report, a global pact called the Montreal Protocol led to the outlawing of CFCs. The ozone "holes" they helped produce over the polar regions are believed to be lessening in size—a rare international victory-in-progress.
That victory may not have happened without the backing of two conservative, anti-regulatory giants, British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher and U.S President Ronald Reagan.
The closing line of the report's executive summary may sound distressingly familiar. "The time to prevent this (disastrous) outcome is running out. … Unless nations take bold and imaginative steps … (we) must accept a troubled entry into the Twenty-first Century."
And one-fifth of the way through that century, here we are.
Peter Dykstra is our weekend editor and columnist.
His views do not necessarily represent those of Environmental Health News, The Daily Climate or publisher, Environmental Health Sciences.
Contact him at pdykstra@ehn.org or on Twitter at @Pdykstra.
Banner photo: President Jimmy Carter at his desk in the Oval Office in 1977. (Credit: Jimmy Carter Library)