New evidence links heavy metal pollution with wildfire retardants
“The chemical black box” that blankets wildfire-impacted areas is increasingly under scrutiny.
Wildfire retardants, the hot-pink mix of water and chemicals sprayed from airplanes by the U.S Forest service to combat wildfires, are under scrutiny after a recent study found they’re a serious source of heavy metal pollution in the U.S.
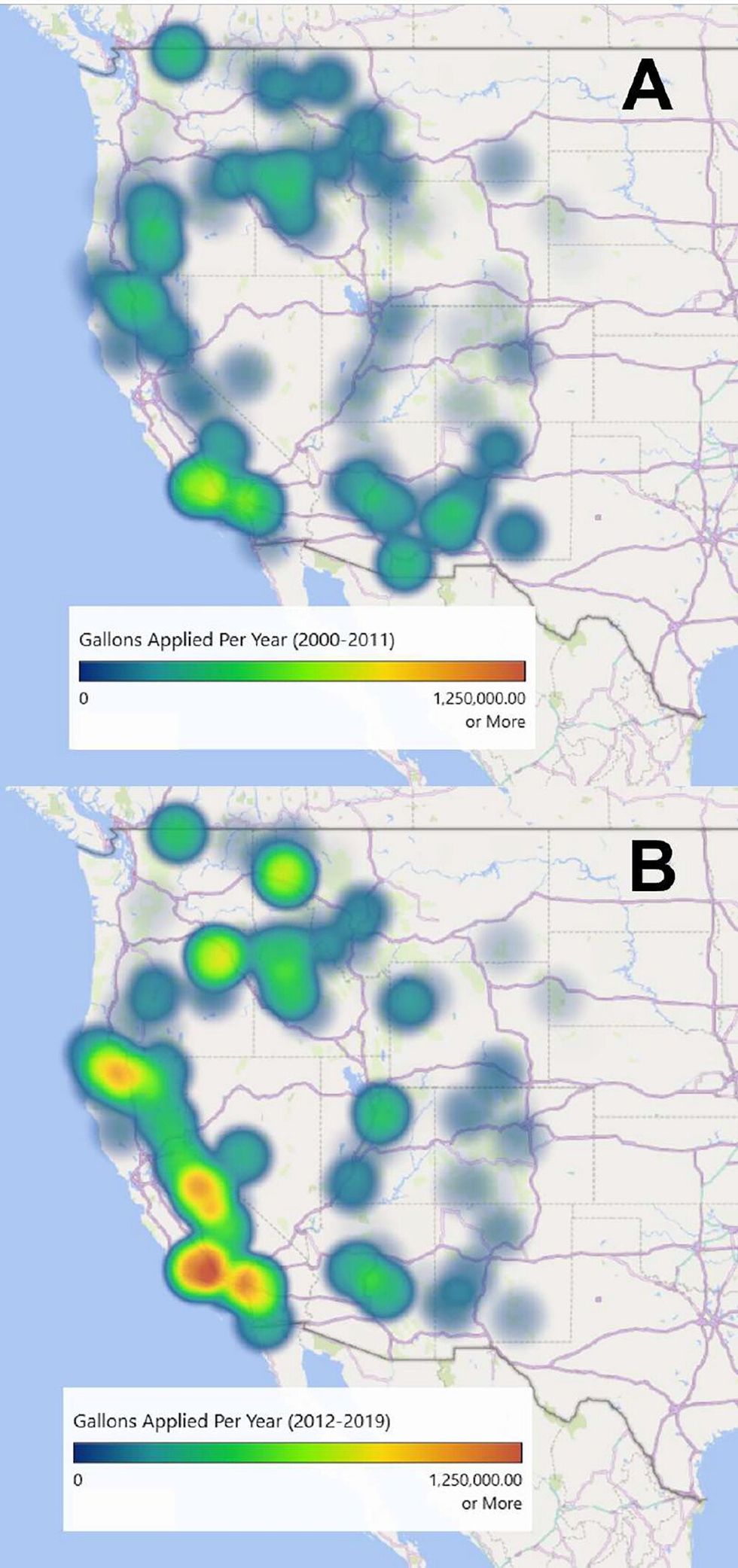
The research, conducted by a team from the University of Southern California and published in Environmental Science & Technology Letters, found that between 2009 and 2021, wildfire retardant application in the U.S. released at least 380,000 kg (more than 400 tons) of at least four toxic metals into the environment. Toxic metals — like cadmium, chromium and vanadium — accumulate in ecosystems and organisms and are linked to organ damage, cancer and neurological disorders.
“The heavy metals report from [the University of Southern California] has been a catalyst. It has created internal discussions about using these retardants,” Andy Stahl, the executive director of the nonprofit watchdog group Forest Service Employees for Environmental Ethics (FSEEE), who was not involved with the study, told EHN.
Wildfire retardant is composed of about 85% water, 10% fertilizers and a mix of other undisclosed ingredients that sticks to plants and depletes the fire of oxygen. This study cracks open the “chemical black box” of the proprietary, undisclosed ingredients in wildfire retardants, according to Stahl.
Between 2009 and 2021, over 440 million gallons of fire retardant were sprayed from airplanes onto federal, state and private land, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture. Most of it was applied in the western U.S., where the area burned by wildfires has increased by eight-fold over the past four decades.
The new research comes as the Forest Service stretches its capacity to put out multiple fires in the Los Angeles area, two of them ranked among the most destructive and deadly blazes in California’s history. Since January 7, the fires have destroyed at least 15,000 structures and killed 28 people. On Wednesday, January 22, a new fire broke out near Castaic, north of Los Angeles.
Firefighters have argued that retardants are an important tool for protecting communities and slowing down fire. “Without aerially applied fire retardant to slow the growth of more isolated fires, potential exists for some of these fires to grow larger before firefighters can safely fight the fires,” a Forest Service report from 2011 reads.
However, a series of lawsuits brought by FSEEE that date back to 2004 have called into question the chemicals’ potential impacts on wildlife and water pollution. In 2008, a federal judge ordered the Forest Service to conduct a study of wildfire retardants’ environmental impacts. In 2011 the study was published, finding that aerial retardant posed a risk to amphibians, rodents, insects and species whose habitat is limited to small geographic areas. As a result, the Forest Service enacted "exclusion zones" where retardant would not be used and established a 300-foot buffer when applying retardant around surface water by plane.
“That fiction lasted until they realized they missed a lot of times,” Stahl said.
The Forest Service data shows the agency has violated its own restrictions 457 times on National Forest System lands since 2012. Of those, 213 intrusions have landed partially in water, either “to protect human life or public safety” (23 intrusions) or by accident (190 intrusions). These intrusions, the FSEEE argued in a 2022 lawsuit, violated the Clean Water Act.
A year later, a US District judge partially agreed with the employees, ordering the Forest Service to apply for a permit from the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to regulate the spraying. The permitting process might take years, so the judge also ordered the Forest Service to report back every six months about the state of the permit. “They’re one-sentence reports, ‘we have asked the EPA for a permit.’ That’s the report,” Stahl said.
In fire-devastated areas, damaged pipes can suck in smoke, and plastic pipes can melt and release harmful chemicals into water, causing spikes in concentrations of harmful chemicals like benzene and other carcinogens. The evidence of heavy metals’ presence in wildfire retardants, Stahl argued, adds to the burden these chemicals might be posing to water treatment systems.
Heavy metals precipitate to the bottom of the cleaning ponds of these systems, concentrating in a sludge that is often sold to farmers across the country to spray on farmland. Other harmful chemicals, like PFAS or “forever chemicals”, which have been associated with birth defects, cancer and developmental delays, have also been found in sewage sludge. “Now [we realize] it may have heavy metals at superfund levels,” Stahl said.
“The challenge for the Forest Service is they’ve done such a good job marketing this magic red elixir, that it's hard for them to back away from it and say, ‘oh, it turns out that the stuff we've been pouring all over your forests and your backyards and your residential areas is actually poisonous,’” Stahl said.