Environmental justice advocates find hope, healing and community in Pittsburgh
Advocates and researchers gathered to not only discuss ongoing fights but victories, self-care and cautious optimism about the path ahead.
PITTSBURGH — Environmental justice advocates gathered last week to celebrate progress and chart a path to the future while focusing on healing, self care and mental health.
May is Mental Health Awareness Month, and the Environmental Justice Summit highlighted the need for self-care and connection among researchers and advocates working to advance justice. Exposure to pollution and anxiety about climate change can negatively impact mental health and people who work to right injustices face the risk of compassion fatigue and burnout.
The summit was conceived and organized by Tina Ndoh, associate professor of environmental and occupational health at Pitt's School of Public Health, and Dani Wilson, executive director of the Cancer & Environment Network of southwestern Pennsylvania.
“Advancing justice is emotionally difficult work,” Wilson told EHN. “Taking care of ourselves and each other is critical to fostering moments of joy and connection that help us stay in the movement.”
Over three days, attendees strategized about how to advance environmental justice in the greater Pittsburgh region and how to foster resilience with tools like meditation, storytelling, community-building, yoga, crafting and cooking. The event also highlighted the importance of humor, connection and optimism.
“This is a social movement,” said Jamil Bey, founder of the nonprofit think tank UrbanKind Institute and newly-appointed director of the Department of City Planning for Pittsburgh. “That means that as part of this work, we’ve gotta have fun with our friends. We’ve gotta stay connected and be able to laugh.”
On Friday, Dr. Sacoby Wilson, an environmental health scientist, professor and director of the Center for Community Engagement, Environmental Justice and Health at the University of Maryland, set the tone for the day by declaring himself a “hardcore Steelers fan” and waving a Terrible Towel above his head while shouting “Go Steelers!”
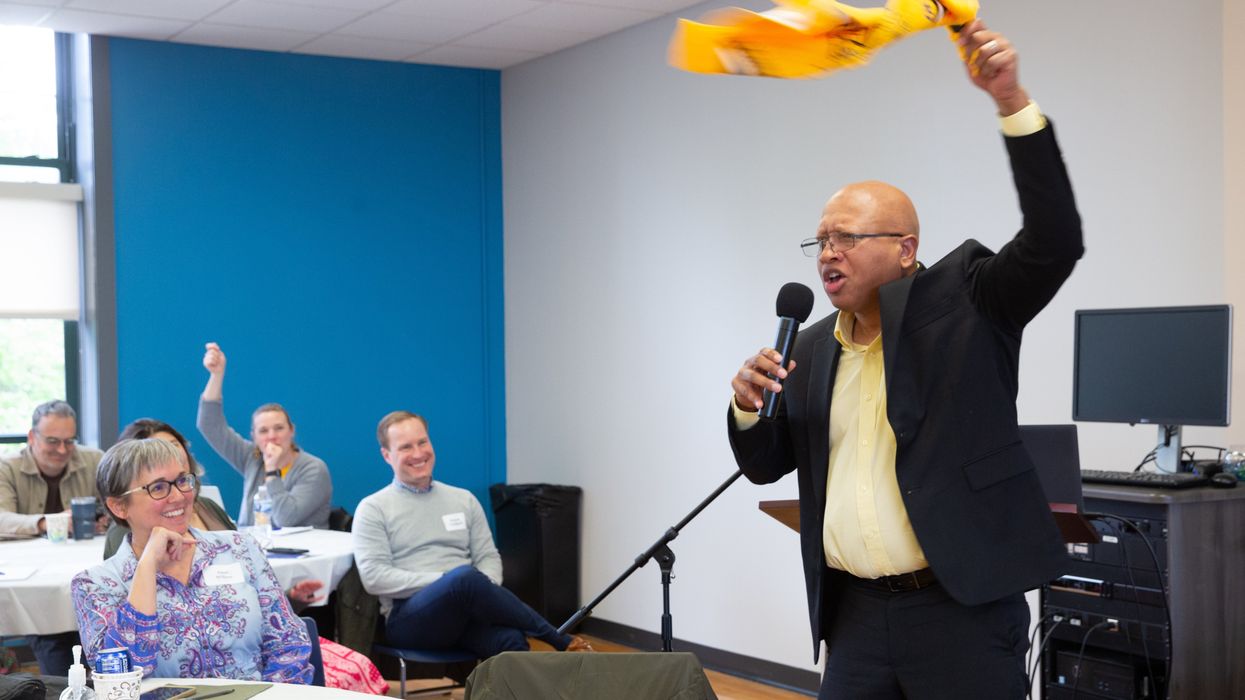

Dr. Sacoby Wilson, an environmental health scientist, professor and director of the Center for Community Engagement, Environmental Justice and Health at the University of Maryland, waves a terrible towel at the EJ Summit Pittsburgh.
Credit: John Altdorfer, courtesy of the Cancer and Environment Network of SWPA
Wilson peppered an otherwise serious talk about the ravages of environmental racism and his work developing tools to combat it with football jokes, referencing recent quarterback drama (“two quarterbacks are better than one!”), emphasizing the importance of both offense and defense for communities burdened by pollution and quipping that if we want to score a touchdown, the community needs to work as a team.
“Where you live can kill you,” Wilson said, noting that poor, Black and Brown neighborhoods in most places, including southwestern Pennsylvania, face higher levels of exposure to pollution that result in worse health outcomes and lowered life expectancy. These places are also more likely to experience the impacts of climate change and other disproportionate harms.
“We need a holistic framework for environmental justice that also acknowledges the need for housing justice, economic justice, social justice, educational justice, reproductive justice and racial justice,” he said, “because these things are all connected. And you can’t get equity without justice… And on a separate note, we’re going to the Super Bowl this year, right?”
Environmental justice victories

EJ Summit attendees show off their artwork.
Credit: Stephanie Ciranni, Cancer Bridges
Other speakers shared recent victories and progress.
Professor Tiffany Gary-Webb, the associate dean for Diversity, Equity and Inclusion at the University of Pittsburgh School of Public Health, shared the results of her work with the Black Environmental Collective and the Black Equity Coalition. The group formed in April 2020 to ensure an equitable response to the COVID-19 pandemic in Pittsburgh and has evolved to continue advancing racial equity in western Pennsylvania.
“We used data to try and understand where there were higher rates of COVID and sent those to the county and state health departments. We talked to elected officials and put out our own dashboard with the numbers for Black populations, and through those efforts we were able to get critical resources to our communities and see that data change,” Gary-Webb said, pointing to a study that summarized the group’s effectiveness. “Now we’re continuing that work with a focus on other issues in our communities.”
Ash Chan, a farmer and steward at Oasis Farm and Fishery, shared their experience working at a Black-owned garden and market in Pittsburgh’s predominantly Black, working-class Homewood neighborhood, which has a long history of disinvestment and has been without a grocery store since 1994. The organization uses vacant land to grow food and offers classes in urban farming and healthy cooking.
“We see food as a driver of social and economic capital, as well as a way that connects people to their cultural roots and their natural environment,” Chan said. “We’re growing what folks want. For example, last year we noticed that elders in the community would line up for okra before we even opened our farmer’s market …so this year we’re growing six different kinds of okra based on that demand.”
Bearing witness to injustice
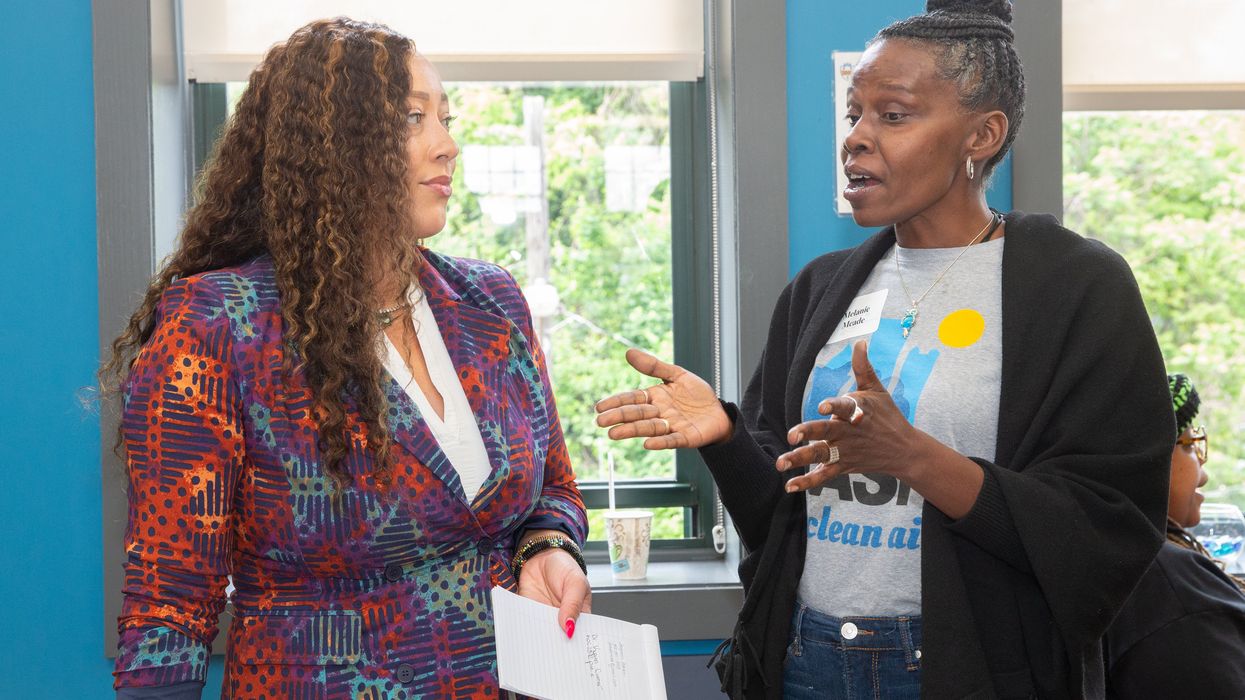

Kayien Conner (left) and Melanie Meade (right) at the EJ Summit.
Credit: John Altdorfer, Cancer and Environment Network of SWPA
While the Summit highlighted progress and promoted resilience, it also emphasized “bearing witness” — a process described by event organizers as actively listening, not looking away, and most importantly, responding — to “the slow violence of environmental degradation on our land.”
Participants were invited to attend a “bearing witness ceremony” in Clairton, a small town about 30 miles south of Pittsburgh that regularly sees some of the most polluted air in the country due to emissions from a coal-based U.S. Steel plant.
“The injustices are very thick and very brutal in Clairton,” said Melanie Meade, a clean air activist and resident of Clairton. Meade shared the heartbreak she has experienced learning that Clairton’s rate of childhood asthma is more than double the national rate, watching many loved ones die of cancer and witnessing the impacts of poverty and violence. “The people are tired and they are sick and they are in great need, and we need to stand in the way for them.”
Later in the day, Kayien Conner, a professor at the University of Pittsburgh’s School of Social Work, told Melanie she’d been moved by her words and asked if she could connect her with an organization she’s involved with that offers mental health resources for Black communities to get additional resources to Clairton.
“Yes, please, thank you!” Melanie said.
“See? We’re here making connections, collaborating, getting this work done already!” Wilson shouted to applause and laughter.
Political optimism
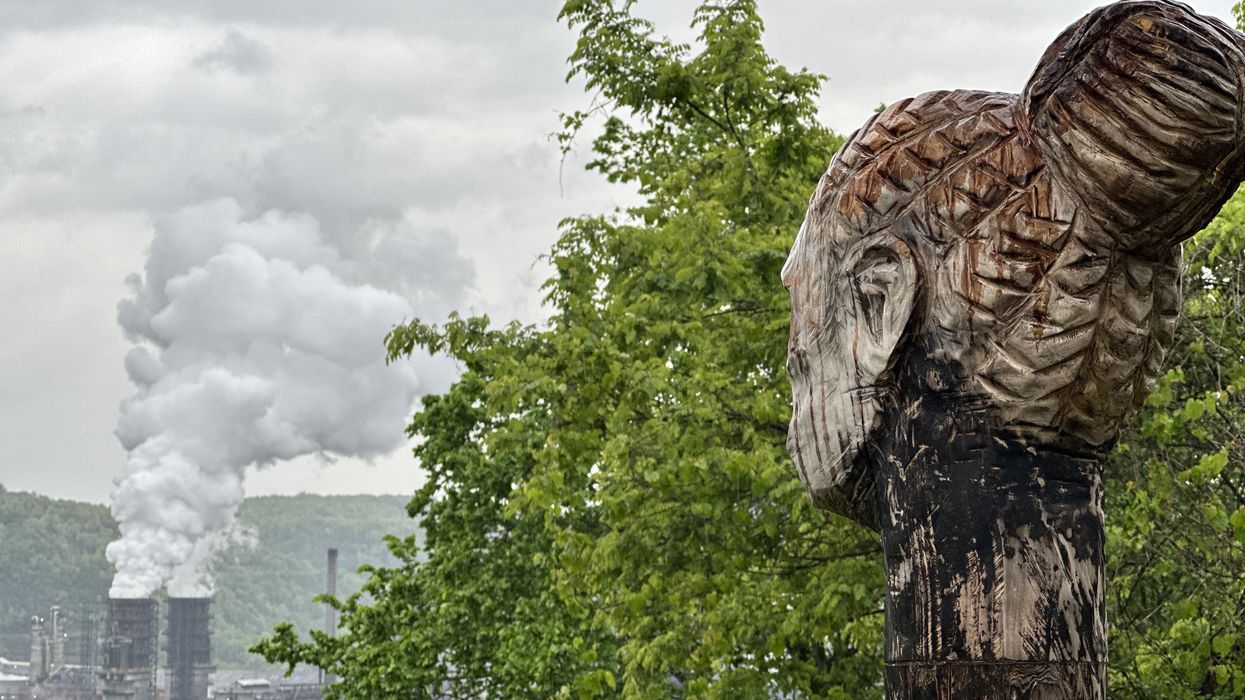

Bearing witness ceremony in Clairton, Pennsylvania.
Credit: Dani Wilson
Speakers at the symposium also noted that western Pennsylvania is on the precipice of major political changes that offer many reasons for optimism for environmental advocates, pointing to the election of progressive politicians like Summer Lee and Lindsay Powell and county executive Sara Innamorato, all of whom have pledged to prioritize environmental justice.
“We’re really shaking things up politically right now,” said Bey. “If we don’t do this now, then that’s on us. Now is the time. Let’s keep lifting each other up, let’s do our work and let’s get this done.”