Op-ed: When a home is not a sanctuary but a sickening, expensive trap
Expensive utilities and pests are deeply intertwined. Why is no one talking about it?
When I tell people I study the relationship between energy justice and wildlife, a look of confusion usually appears. “What does energy have to do with wildlife and justice?” they ask.
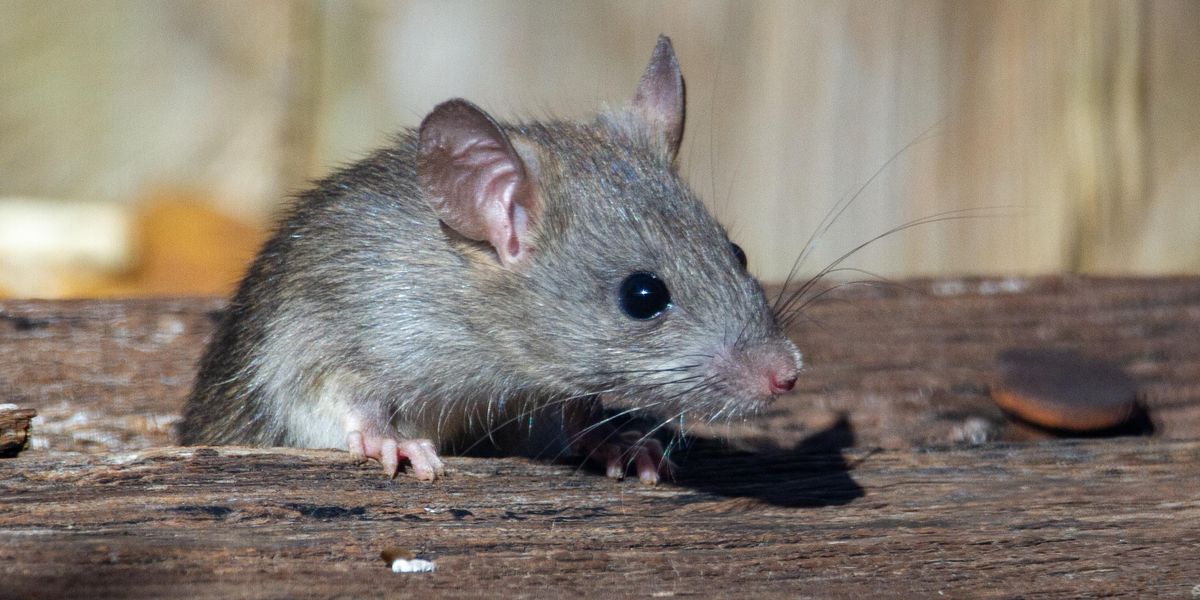
My response is always the same: think about how rodents and other pests get inside your home. Broken windows, gaps under doors, crumbling foundation, little to no insulation – the same features that make efficient heating or cooling difficult.
Minority communities, I then tell them, often don’t have the money to improve their homes, which leads them to struggle to pay expensive utilities bills. Crumbling homes also means residents are disproportionately exposed to rodents and other pests, alongside the pathogens they carry –from Hantavirus and Leptospirosis to Typhus.
This essay is also available in Spanish
Confusion turns to frustration. How could something so intuitive go unnoticed? Can families living in inefficient housing do anything to protect themselves?
As a trained ecologist with experience in energy and housing, I’ve seen how allowing pest species to proliferate in homes where energy use is inefficient further jeopardizes the health of people already experiencing cardiovascular and pulmonary disease. Buildings that are either too hot or too cold and expose people to disease from rodents are linked to poor health, and families often have to choose between food and medicine or paying high energy bills to keep living in that sickening environment.
Ecologists and energy researchers have yet to come together to study these links. The siloed thinking stagnates our understanding of these issues and stops us from designing complex and adaptive solutions to rodent infestations.
Why is an ecologist talking about energy and health?
I began to make sense of these questions in late 2019. After struggling to break into the scientific community, I became an urban ecologist at the Applied Wildlife Ecology Lab at the University of Michigan. I conducted wildlife surveys and diet analysis, and while I enjoyed my work, I felt I wasn’t living up to a core belief: that science is ‘not just science.’ I believe it is one’s civic duty to stand up to injustice. Unsatisfied by the answers within the field, I joined the Urban Energy Justice Lab at the University of Michigan, which specializes in solving the world's emerging energy concerns. There my journey through people’s homes began.
I entered homes in Detroit, and while measuring the air pollution inside them, I asked residents about their health and the strategies they used to cope with energy inefficiency to assess their quality of life. As I built relationships with residents, they shared stories of wildlife in their homes, including mice and raccoons, including one elderly woman who explained that they only recently eradicated a family of raccoons living in their attic. These pests not only exacerbated asthma, but also caused significant physiological stress.
To my surprise, the only data on this phenomenon was the American Housing Survey finding that people living in homes with cracked inside walls were four times more likely to report rodent sightings. Later, I would obsessively look for anything connecting these issues: from exterminator blogs, National Park brochures, to a few academic papers discussing denning sites in urban areas for raccoons and foxes. But I found nothing concrete. It was shocking that an issue ripe for interdisciplinary collaboration was not a topic of discussion among my colleagues.
How did energy injustice and rodent infestations become a problem?
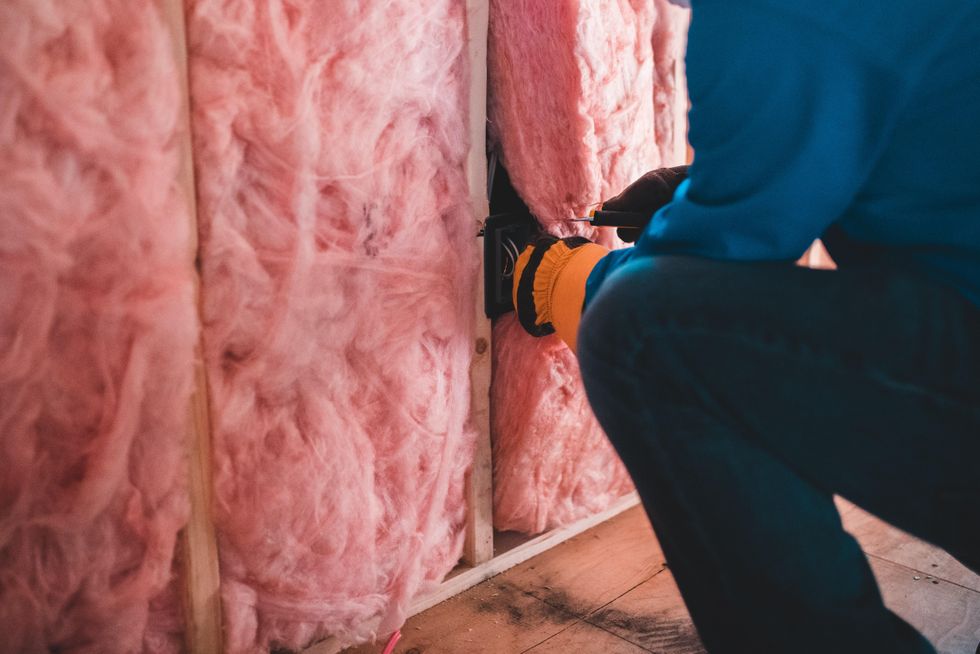

Broken windows, gaps under doors, crumbling foundation, little to no insulation are all features that make efficient heating or cooling difficult — and allow rodents into homes.
Credit: Erik Mclean/Unsplash
The inaction on rodent infestations and their relationship to energy justice starts with how cities create their infrastructure, energy and wildlife policies. Many homes either start off poorly built or become inefficient as they decay and building material becomes easy to penetrate. It is no surprise that old and often derelict houses are synonymous with large cities, and rodents seemingly have evolved to take advantage of that failure. As opportunistic rodents looking for a warm nesting site away from predators find their way inside homes, a single animal can quickly become an infestation. A rat can squeeze through a gap the size of a quarter, though often, entry points of foundation gaps and exhaust vents are much larger, allowing for easy access. Once rodents like brown rats are inside, they can lead to much more damage, including chewing through wiring, causing fires, contaminating food and shedding allergens and viruses. America’s inability to fix infrastructure, and policies that reward new and cheaply built housing, only exacerbates the challenge of keeping rodents out of homes.
Urban rodents like brown rats and house mice are not considered wildlife by cities, rather pests—due to this arbitrary classification, they often fall into the jurisdiction of vector control, a framework that doesn’t always work. Toxic bait called rodenticide is often used, despite its lackluster success killing rodents and significant risk to animals preying on rodents who've ingested the bait. Cities’ efforts to reduce rodent populations in public and private spaces are futile until they incorporate pest management programs that include removing trash and sealing infrastructure where rodents like to hide.
While an integrated pest management strategy has been touted as the golden standard by entomologists and exterminators since as early as 1944, the federal government still needs to recognize it as an effective strategy for pests in cities. This is unlikely to happen as recent budget cuts and organizational changes have significantly reduced funding for integrated pest control.
As buildings decay and become perfect refuges for pests, they become less than ideal homes for humans from an energy efficiency standpoint – nearly a third of households spend more than 10% of their income on heating and cooling. While there is assistance for families, they require high levels of poverty to qualify, have limited funding, narrow scopes of assisting and long wait times. Likewise, there is no requirement to know the energy efficiency of a building, or mandates to retrofit homes to acceptable efficiency levels. As a consequence, there are likely many residents, including renters, living in and paying for inadequate housing that can jeopardize their health with little to no recourse.
What can we do about energy injustice and rodents in homes?
We need to bring together architects, city planners, health officials, energy scholars, economists and ecologists. Together we can start by understanding how many pests (and what diseases they carry) infiltrate inefficient homes in a given year. From there, federal and local agencies can allocate more money to deep retrofits that fix all aspects of a home’s inefficiency with high grade rodent proof materials. Too often, well-meaning programs don't deeply retrofit homes because of a lack of funding, meaning homes are barely efficient and do little to exclude pests.
Retrofitting so many homes is a monumental undertaking, but it must occur if we want to see neighborhoods and homes that are just and healthy. City planners should also assess how homes and greenspace intersect, evaluating if park amenities like fruit bushes attract coyotes and foxes that also prey on rodents, or where to locate closed trash cans that keep rodents at bay.
Cities are unlikely to eradicate rats and mice. They are intelligent, prolific breeders and, with generalist diets, can live eating almost anything. However, it is time that we stop normalizing their presence in cities and stop pretending solving inadequate housing is a matter of giving money to vulnerable people to pay utilities.
A home should be a sanctuary. However, for many low-income residents, their home can be a nightmare that makes them sick, costs money and lowers their quality of life. Inefficient homes torment the human body. The environmentally just future we need is one where all homes, regardless of income or race, are comfortable and pest free, offering peace of mind by keeping loved ones safe.

Gabriel Gadsden is a 2nd year Ph.D. student of Environmental Sciences at Yale University’s School of the Environment, a native of North Carolina, and is interested in the interface of energy justice, urban ecology, and health. For his dissertation, he focuses on how disparities in energy-efficient housing are affecting urban rodent disease and allergen exposure in Philadelphia. Outside his dissertation, he works on expanding the scope of disciplinary paradigms, including broadening the use of various environmental justice initiatives in ecology, challenging perceptions of certain landscapes, and diversifying public science participation. Twitter: @NcredblyDopeSci and LinkedIn: @Gabriel I. Gadsden
This essay was produced through the Agents of Change in Environmental Justice fellowship. Agents of Change empowers emerging leaders from historically excluded backgrounds in science and academia to reimagine solutions for a just and healthy planet.