Peter Dykstra: The Earth Summit to end all Earth Summits
Thirty years ago, the Rio Earth Summit came together to solve our problems. Really?
In 1972, world leaders had gathered in Stockholm in an unprecedented acknowledgement that we were running into trouble. The gathering hammered out a weighty Statement of Principles. It was the first draft of an owner’s manual for planet Earth, but it left much to do.
Two decades later, the site was Rio de Janeiro. World leaders addressed the hopes for Rio:
“There are those who say economic growth and environmental protection are not compatible. Well, let them come to the United States.″ – U.S. President George H.W. Bush
″The ecological debt should be paid, not the foreign debt. Hunger must disappear, not man.” – Cuban President Fidel Castro
“We are ready to assume our share and hope other industrial countries will do the same. ... We are determined to live up to our responsibilities to developing countries.” – German Chancellor Helmut Kohl
″Developed countries have a greater obligation to find solutions and to transfer technology. ... Protection of the environment must respect the sovereignty and independence of each country.” – Chinese President Li Peng
Journalist George Monbiot was a tad more cynical about Rio’s rhetoric and intentions:
“It sounds lovely, doesn’t it? It could be illustrated with rainbows and psychedelic unicorns and stuck on the door of your toilet. But without any proposed means of implementation, it might just as well be deployed for a different function in the same room.”
Agenda 21

One of Rio’s major achievements became – at least in the U.S. – a bizarre political caricature.
Agenda 21 was a visionary, totally non-binding guidebook for environmental action in the 21st Century. It called for concerted action on climate, clean energy, empowerment of women, protection of habitat, abolition of illegal logging and fishing, and much more.
The guidebook may have been unrealistic on the very day it was published, but in the U.S., far right media figures and politicians saw Agenda 21as the guidebook for the sinister one-world government they’d always warned about.
Radio/TV firebrand Glenn Beck branded the document, which was endorsed by Bush the Elder and 177 other heads of state, as the Scripture for a new religion. Senator Ted Cruz cited the Agenda’s call for the abolition of golf courses, grazing land and paved roads. Others said Agenda 21 prescribed genocide as a population control measure.
Of course, scholars who had actually read Agenda 21 could find no hint of these things.
Failed Kyoto Protocol
The most famous and enduring product of Rio was the U.N. Framework Convention on Climate Change, (UNFCC) which begat annual climate confabs which begat 1997’s Kyoto Protocol. The Agreement was under fire from the start for its sole focus on industrialized nations. Developing nations, even giants like India and China were let off the hook, with no requirements to reduce carbon emissions.
Kyoto came under intense fire in U.S. political circles for its apparent double standard. The Senate, charged with ratifying treaties, held a non-binding vote on Kyoto. It lost 95-0. President Clinton never submitted Kyoto for a formal vote. With India and China excused and the U.S. playing hooky, Kyoto was never fully taken seriously.Global climate talks
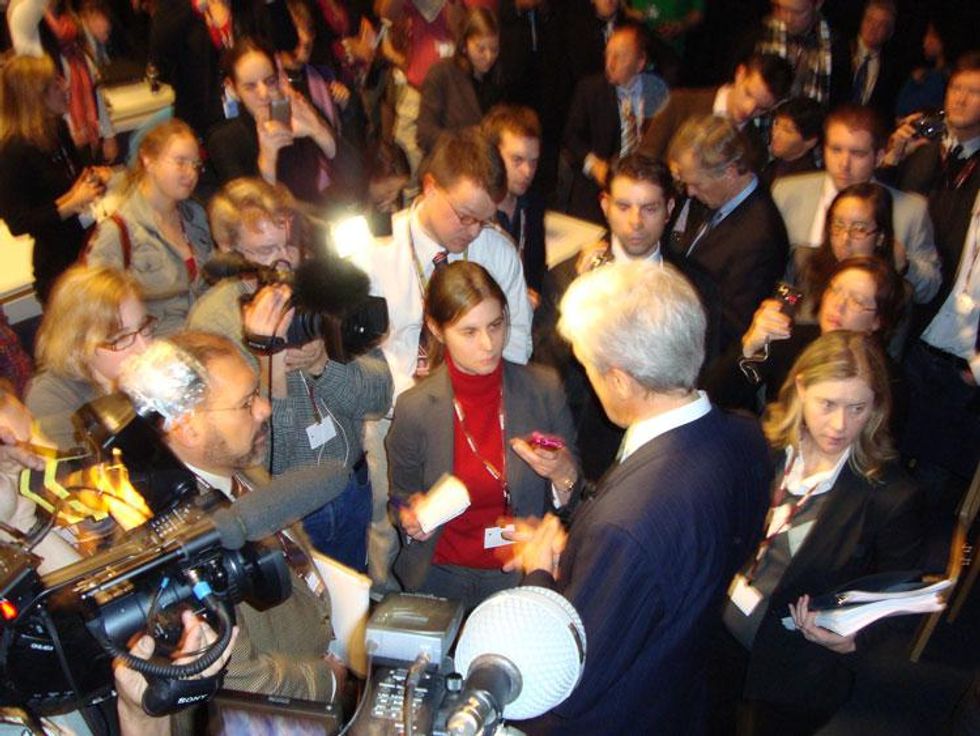 Douglas Fischer / EHS
Douglas Fischer / EHSUNFCCC also brought us the COPs. That would be the annual Conference of the Parties, known to most everyone as the "UN climate talks." Crucial meetings included the 2009 Copenhagen COP, where high hopes for progress were both dashed and overshadowed.
Climate denial groups released what they said were the highlights of thousands of climate scientists’ emails, suggesting that climate science was a cynical scam. Multiple investigations eventually cleared the scientists of everything except poorly-chosen email language and a little juvenile humor.
In the 2015 Paris COP, the Parties had reason to, ummmm, celebrate an agreement that saw comparatively strong commitments to greenhouse gas reductions. This was partly due to a strong showing from Obama’s Secretary of State, John Kerry.
Flip to climate denial
Of course, Donald Trump’s capture of the White House in 2016 flipped the U.S. into the denier camp.
Rio also saw the creation of the Convention on Biological Diversity, a quiet but vital body that monitors and identifies ecological hotspots; and the Statement of Forest Principles, a first crack at rulemaking for everything from turning the boreal forests into bathroom tissue to turning the Amazon into, well, stuff for sale on Amazon.com.
Rio also brought a new term into widespread use: “Sustainable development” became the buzzphrase for just about every constituency at Rio: If you’re a paper company, “sustainable development” meant how much Charmin you could squeeze onto a roll before you’d entertain the notion of restraining your business.
If you’re an environmentalist, it meant how much restraint you could demand on timber and paper companies. Or whether gasoline prices, closely following 1989’s Exxon Valdez disaster and the first Iraq war, would continue to rise past the inflation-adjusted $1.95 a gallon.
Greenwashing
Greenwashing also came of age at Rio and at the 1990 Earth Day festivities, prompting PR campaigns suggesting that “BP” also stood for “Beyond Petroleum” and British American Tobacco’s acronym also stood for “A Better Tomorrow.”
Make no mistake, the Rio Earth Summit was a good thing. It focused worldwide attention on environmental problems and solutions in a way that doesn’t seem to happen anymore. But did it really solve any problems?
It’s 30 years later, and we don’t know yet. And that’s a problem.
Peter Dykstra is our weekend editor and columnist and can be reached at pdykstra@ehn.org or @pdykstra.
His views do not necessarily represent those of Environmental Health News, The Daily Climate, or publisher Environmental Health Sciences.