EPA seeks to slash chemical plants’ cancer-causing emissions
Major updates to air pollution regulations could reduce frontline communities’ excess cancer risk by 96%.
In April, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency proposed a package of updates to the Clean Air Act that could dramatically decrease dangerous air pollution.
The proposal, which applies to roughly 80 different toxics, will enhance regulations for 218 chemical facilities across the country, cutting 6,000 tons of harmful air pollution each year.
A key mandate will require on-site air monitoring for the estimated 128 chemical plants that emit one or more of six cancer-causing pollutants, including ethylene oxide, used to sterilize medical equipment, and chloroprene, used in the manufacture of the synthetic rubber neoprene. The updated regulations stand to cut national emissions of ethylene oxide by 63% and chloroprene by 74%. Overall, frontline communities’ excess risk from inhaling these hazardous chemicals is expected to drop by 96%, the EPA indicated.
Despite the well-documented health risks of these air toxics, state and federal agencies have largely relied on plants to self-report their emissions — a system rife with abuse, advocates say. In the last three years alone, 80% of these facilities have violated environmental laws, according to an analysis by the Environmental Defense Fund. Several companies, including the chemical giants Dow, Formosa Plastics and DuPont, have committed multiple significant infractions in environmental justice communities — areas where residents are predominantly people of color or where a substantial portion live below the poverty line.
The proposed rule is “very long overdue,” Dionne Delli-Gatti, the associate vice president for community engagement at Environmental Defense Fund, told Environmental Health News (EHN).
“There has been a history of pretty significant noncompliance,” she said. “You’re not talking about the mom-and-pop shops; you’re talking about companies and facilities that are owned by large corporate conglomerates that do have the funding to ensure compliance.”
Increased monitoring, increased accountability
Mandating fenceline monitors — air pollution sensing devices located on a plant’s property line — will make it harder for chemical companies to hide their emissions, Jennifer Hadayia, executive director for Air Alliance Houston, told EHN. While regional air monitoring networks exist, they’re not designed to detect every pollutant of concern and can be many miles away from chemical facilities — making it virtually impossible to know what plants are emitting which toxics and in what amounts. “Monitors that are literally picking up the emission in real time at that facility’s perimeter,” Hadayia said, “are one of the only ways we know what is truly being emitted in our community.”
Facilities whose fenceline emissions exceed new, federally determined levels will be required to find leaks and make repairs. In addition to fenceline monitoring, the EPA proposal introduces a slew of other changes and additions to the Clean Air Act. These include rules to reduce emissions from flaring — which occurs when chemical plants burn air toxics to destroy them — and improved regulations for dioxins and furans, highly toxic substances emitted from chemical plants and other sources.
The new proposal, an EPA spokesperson told EHN via email, would also “remove general exemptions from emissions control requirements during periods of startup, shutdown and malfunction.” In Texas, Hadayia explained, companies are currently allowed to exceed their permitted air pollution levels for any length of time during emergencies or repairs — events left to companies to define or report. “That emergency situation doesn't have to be proven. It doesn't have to be documented,” Hadayia said.Communities at risk
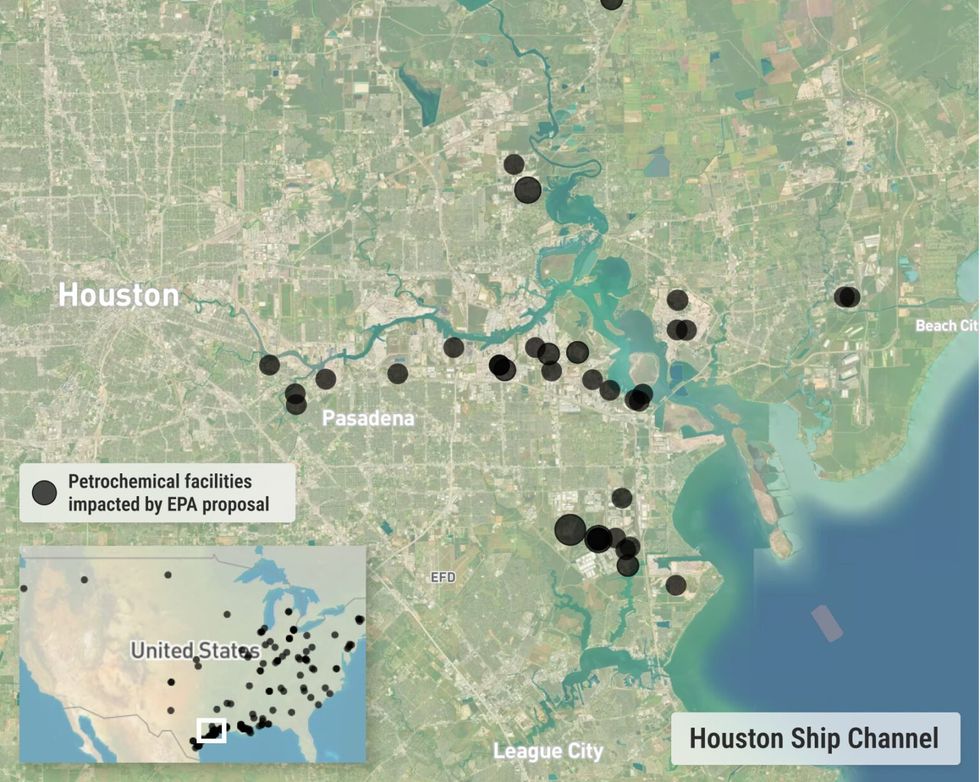
While the affected facilities are located across the country, major clusters are found in Louisiana and Texas. Of the chemical plants regulated under the EPA proposal, 15% are in Houston alone, Hadayia said. Houston is home to nearly half of U.S. petrochemical capacity and is the nation’s third-largest hotspot for cancer-causing air pollution, according to the investigative reporting outlet ProPublica.
Along the Houston Ship Channel, a dense concentration of oil refineries, plastic manufacturing facilities and other chemical plants exposes residents to a hazardous mix of air toxics. In cities along this corridor, such as La Porte and Port Neches, excess cancer risk ranges from three to six times EPA-determined limits, ProPublica found.
Louisiana’s “Cancer Alley,” however, has the grim distinction of having the nation’s highest levels of carcinogen-laced air. Residents of some parts of this chemical corridor, an 85-mile stretch along the Mississippi River between New Orleans and Baton Rouge, are subject to a cumulative cancer risk 47 times what the EPA considers acceptable, ProPublica reports. Industrial emissions in Louisiana are seven to 21 times higher in communities of color, according to a 2022 report. A related 2022 study found that the state’s impoverished and Black communities face measurably higher cancer rates from air pollution.
Residents in affected areas can learn more about their cancer risk from ethylene oxide, chloroprene and other air pollutants, as well how this rule will impact local chemical facilities, by viewing an interactive map put together by the Environmental Defense Fund. Fenceline monitoring data will be publicly available through the EPA’s WebFIRE database.
“I think that probably the most important aspect of this rule is giving frontline communities, and agencies as well, the information necessary to ensure stronger protections and to ensure compliance,” said Delli-Gatti.
The new EPA proposal is inspired in part by a 2015 rule that requires petroleum refineries to implement fenceline monitoring for benzene, a hazardous chemical linked to leukemia and bone marrow damage, among other risks. Benzene concentrations have dropped an average of 30% since the program began, “illustrating that fenceline monitoring is an effective tool in reducing emissions on an ongoing basis,” an EPA spokesperson said.
In a statement, the industry trade group American Chemistry Council expressed concerns about the proposed ethylene oxide limits, saying “conservative regulations on ethylene oxide could threaten access to products ranging from electric vehicle batteries to sterilized medical equipment.” The ACC said it is reviewing the EPA’s proposal and will be active in the public comment and review process.
For Hadayia, these updated regulations are crucial for protecting frontline communities in Houston and beyond. “There aren't a lot of things we can prevent in this world,” Hadayia said. “But if we can prevent carcinogens going into the air, then we have an obligation to do so. We believe industry has an obligation to do so as well.”













