We're building the equivalent of Paris every week. That's a problem.
The building and construction sector is booming—and it's costing the planet
The amount of floorspace in buildings around the world—currently about 2.5 trillion square feet—is set to double by 2060, and researchers say this is a major problem for the climate.
A new United Nations report from the Global Alliance for Buildings and Construction released today finds that in order to keep the Paris Climate Agreement goals on track, the construction industry needs to improve energy efficiency per square meter (about 10 square feet) by 30 percent by 2030.
Why it matters
The doubling of buildings over the next 40 years would be like adding the floor area of all of Japan's buildings to the planet every single year to 2060, or a new Paris every five days over the same amount of time.
This means much more climate warming gases. The building industry of course isn't the only cause of climate change but it does account for about a quarter of global greenhouse gas emissions. CO2 emissions from buildings and construction increased by about 1 percent annually between 2010 and 2016.
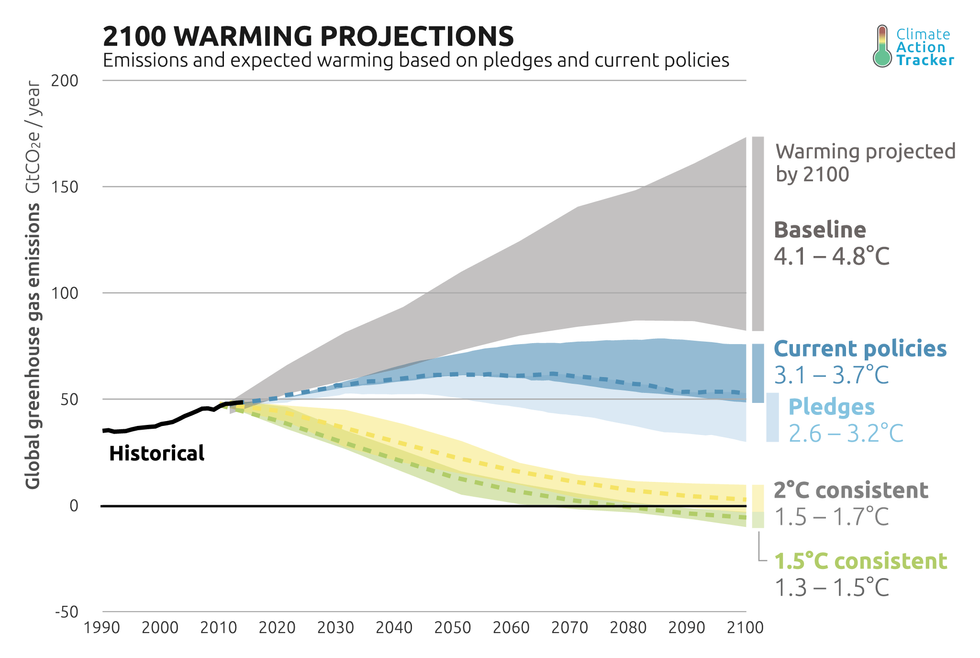
The Paris Agreement aims to limit global warming to 1.5 or 2 degrees Celsius higher than pre-industrial levels. If the agreement falls apart, at current emission levels the planet would warm roughly 4.2 degrees Celsius by the year 2100. This would make some places uninhabitable, trigger sea level rise that would inundate some major cities, and would create real challenges in trying to feed a growing population.
Is there any hope?
Maybe—in order to reach the 30 percent energy efficiency increase, "near-zero energy, zero-emissions buildings need to become the construction standard globally within the next decade," the report found. Also the rate of retrofitting older buildings to become more energy efficient would have to improve from the current 1 to 2 percent per year to more than 3 percent per year.
There's reason for optimism: 132 countries mention the buildings industry in their greenhouse gas reduction plans submitted to the UN. And the new report found that investments in current energy efficiency and low-carbon health and cooling technology could reduce buildings' energy demand by 25 percent.
What experts are saying:
"Similar to many areas linked to the Paris Agreement, the building sector is seeing some progress in cutting its emissions, but it is too little, too slowly. Realizing the potential of the buildings and construction sector needs all hands on deck - in particular to address rapid growth in inefficient and carbon-intensive building investments." -Erik Solheim, head of UN Environment
See the full report, which was led by the International Energy Agency.













